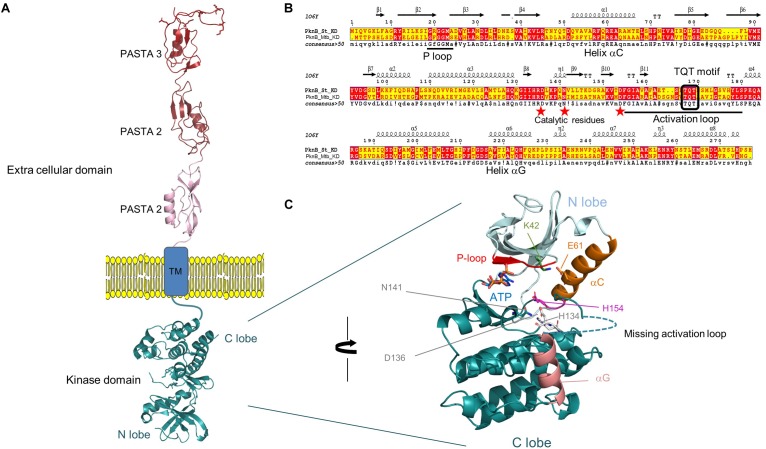
FIGURE 2.
(A) Topology of PknBSt full length, kinase and extra cellular domain (ECD) have been modeled by homology using PknB, and PASTA coordinates from M. tuberculosis and PASTA coordinates of S. aureus. Only the TM domain lacks solved structure and could not be modeled. The PASTA domains are shown extended across the peptidoglycan layer. (B) ESPript alignment of the kinase domain between PknB from S. thermophilus and M. tuberculosis. The structural elements that sign up the hallmarks of Hanks type kinase are conserved and reported in the sequence: helices αC, αG, P- and activation loops. Red stars evidence the catalytic residues. (C) Close view of the kinase domain, with the accommodation of an ATP molecule docked in the active site. The structural and functional elements are highlighted: P-loop in red, αC in orange, its residue E61 forming a salt-bridge with K42 that locks αC in a conformation and participates to create a competent active site are in stick, the active triad composed of H134, H138, and N141 are also shown as sticks. Helix αG is in salmon and the missing activation that could not be modeled because too long and with no reference coordinates is drawn as dotted line. The figure has been prepared using PyMOL2.2 Schrödinger.