Figure 2.
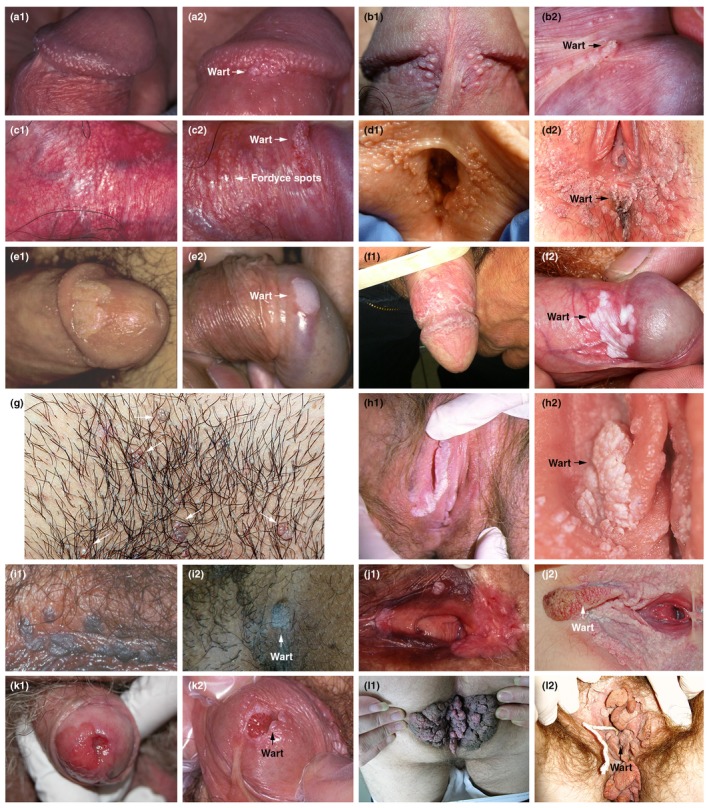
Differential diagnoses (images on the left) of anogenital warts (images on the right). (a) (a1) Pearly penile papules: normal glands on the corona glandis, (a2) AGW: small cluster of warts on the coronal sulcus, (b) (b1) Parafrenular glands: normal glands on either side of frenulum, (b2) AGW: parafrenular glands with wart on the frenulum, (c) (c1) Fordyce spots: fordyce spots in a male, (c2) AGW: fordyce spots alongside a wart, (d) (d1) Papillomatoses of vulva: scattered raised glands can be confused with AGW, (d2) AGW: vulval warts – scattered, soft and fleshy, the vestibular area, (e) (e1) Syphilis on mucosal plates: painless plaque, which suddenly appears on one or more mucosal membranes, (e2) AGW: penile wart, (f) (f1) Lichen planus: whitish, fine reticulate papules on the glans and corpus, (f2) AGW: white wart patch, (g) (g1) Molluscum contagiosum and (g2) AGW (arrows on image show lesions): both pink dome‐shaped papules and warts, (h) (h1) Bowen's disease: whitish plaque on labia minora, (h2) AGW: extensive genital warts, (i) (i1) Pigmented intraepithelial neoplasia: pigmented popular strips that extend to the anogenital area, (i2) AGW: penile pigmented warts, (j) (j1) Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia: pigmented popular strips that extend to the anogenital area, (j2) AGW: extensive soft warts and one large keratinized wart, (k) (k1) Invasive carcinoma of the penis: invasive cancer of the glans of the penis arising from penile intraepithelial neoplasia, (k2) AGW: condylomata acuminata on the urethral mucosa, (l) (l1) Buschke‐Löwenstein: rapid expansion of budding masses that coalesce to form tumours, (l2) AGW: vulval and anal warts.
