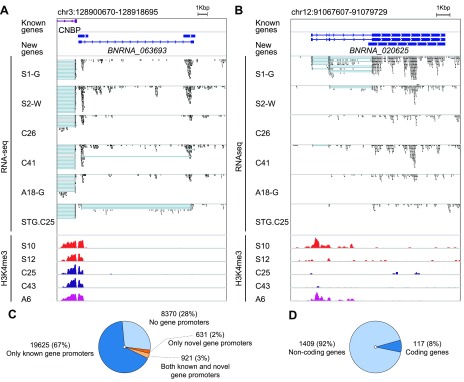
Figure 2.
Integration of H3K4me3 and RNA-seq data identified novel protein-coding and noncoding neuronal genes active in the human brain. A) Novel unannotated ncRNA gene with TSS mapped to the H3K4me3-marked region also harboring a promoter and TSS for the CCHC-type zinc finger nucleic acid binding protein gene. B) A novel ncRNA multiexonic gene with widely variable neuronal H3K4me3 abundance and expression in neurons from different individuals. C) Relative proportion of H3K4me3-marked promoter regions for previously annotated genes. D) Proportion of novel genes with notable protein-coding potential. Sample prefix indicates disease status; suffix indicates tissue for RNA-seq samples. H3K4me3 peaks are color-coded (red, schizophrenia; purple, autism; blue, control). A, autism; C, control; G, cortical gray matter; S, schizophrenia; W, cortical white matter; STG, superior temporal gyrus. For RNA-seq, blue lines show the connection of exons in spliced transcript reads.