Figure 3.
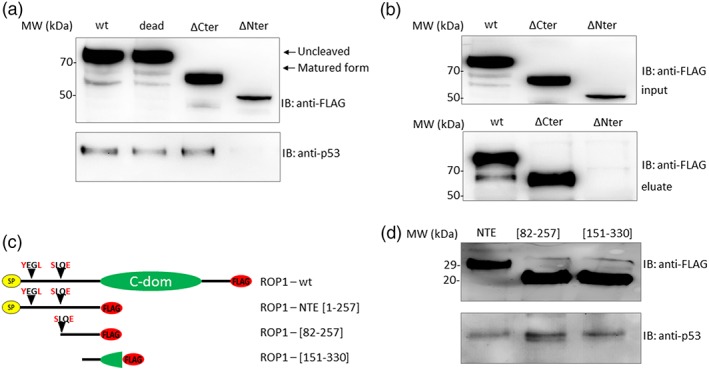
EtROP1 coprecipitates p53 via its NTE domain. (a) Western blot analysis showing host‐cell p53 co‐purification with EtROP1‐FLAG wt, dead, ∆Cter or ∆Nter forms in a pull‐down assay using anti‐FLAG affinity‐chromatography after constructs transfection in HEK293T cells. EtROP1‐FLAG constructs (wt, dead, ∆Cter and ∆Nter; top panel) and p53 (bottom panel) were detected using an anti‐FLAG or an anti‐p53 antibody, respectively. (b) Western blot analysis showing EtROP1‐FLAG co‐purification with a 6His‐tagged p53 recombinant protein in a pull‐down assay. Protein lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with EtROP1‐FLAG constructs (wt, ∆Cter and ∆Nter) (input, top panel) and eluted complexes (eluate, bottom panel) were both detected using an anti‐FLAG antibody. (c) Scheme of EtROP1‐FLAG constructs. NTE corresponds to the N‐terminal extension domain of the protein (residues 1 to 257), [82–257] corresponds to the amino acid sequence between the maturation site (SLQE) and the beginning of the catalytic domain (residues 82 to 257) and [151–330] corresponds to the end of the NTE domain and the beginning of the catalytic domain (residues 151 to 330). (d) Western blot analysis showing host‐cell p53 co‐purification with EtROP1‐FLAG NTE, [82–257] and [151–330] forms in a pull‐down assay using anti‐FLAG affinity‐chromatography after constructs transfection in HEK293T cells. EtROP1‐FLAG constructs (NTE, [82–257] and [151–330]; top panel) and p53 (bottom panel) were detected using an anti‐FLAG or an anti‐p53 antibody, respectively
