Figure 2.
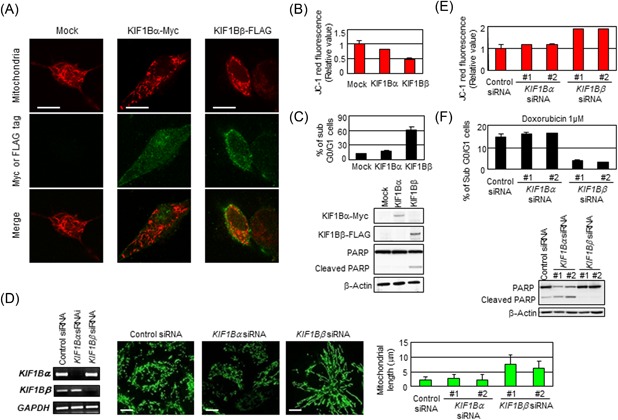
Deficiency in KIF1Bβ yields mitochondrial fusion. A, Add‐back of KIF1Bβ reverts spontaneous mitochondrial fusion in NB‐1 cells. NB‐1 cells were transfected with empty vector (Mock), KIF1Bα‐Myc, or KIF1Bβ‐FLAG expression vectors. After 48 hours, mitochondria are visualized by MitoTrackerRed CMXRos. B, Add‐back of KIF1Bβ decreases membrane potential. The average values of JC‐1 red fluorescence are measured in NB‐1 cells and shown as the normalized values by the value obtained from control. *P < 0.05 (n = 3). C, Add‐back of KIF1Bβ attenuates drug resistance. NB‐1 cells transfected with KIF1Bα or KIF1Bβ were treated with doxorubicin. Apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry and immunoblotting. D, Knockdown of KIF1Bβ results in mitochondrial fusion. HeLa cells were transfected with a scramble siRNA (control) or two kinds of specific siRNAs against KIF1Bα or KIF1Bβ for 48 hours. Knockdown efficiency was confirmed by semiquantitative RT‐PCR (left panel). Morphological changes in mitochondria were observed by indirect immunofluorescence using the BacMam‐GFP mitochondrial probe (green). Scale bar, 25 µm. The average mitochondrial length was measured (right panel, n = 100). E, Knockdown of KIF1Bβ increases membrane potential ΔΨm. The values of JC‐1 red fluorescence in the cells in (D) were measured and shown as the normalized values by the value obtained from control. F, Knockdown of KIF1Bβ inhibits apoptosis induced by doxorubicin. After the siRNA knockdown, HeLa cells were treated with 1 µM doxorubicin for 48 hours. Apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry and immunoblotting. RT‐PCR, real‐time polymerase chain reaction; siRNA, small interfering RNA [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
