Figure 6.
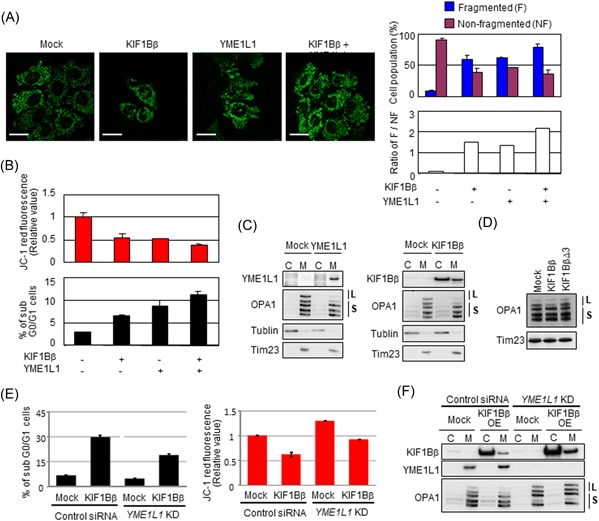
KIF1Bβ promotes mitochondrial fragmentation through binding YME1L1. A, Coexpression of KIF1Bβ and YME1L1 promotes mitochondrial fragmentation. HeLa cells were transfected with KIF1Bβ, YME1L1 or both, and mitochondrial morphologies were visualized with BacMam‐GFP mitochondrial probe (green). Cell population (%) harboring fragmented mitochondria and nonfragmented mitochondria, as well as their ratios (white bars), are also shown (n = 100). B, Coexpression of KIF1Bβ and YME1L1 induces apoptosis. Cells in (A) were used for mitochondrial membrane potential ΔΨm (top panel) and FACS (bottom panel) analyses. C, Overexpression of either YME1L1 or KIF1Bβ induces the cleavage of the long forms of OPA1. Cells transfected with each expression vector were used for subcellular fractionation. D, The death‐inducing region of KIF1Bβ is necessary to cleave the long forms of OPA1. HeLa cells were transfected with full‐length KIF1Bβ or KIF1BβΔ3 expression vectors for 48 hours and mitochondrial fractions were prepared for immunoblotting. It should be noted that the largest form of OPA1 (top band) occasionally receives spontaneous cleavage, and thus it disappears regardless of experimental conditions. E, Depletion of YME1L1 protects from KIF1Bβ‐induced cell death and decreases membrane potential ΔΨm. KIF1Bβ was overexpressed in YME1L1‐knocked down HeLa cells. These cells and control cells were used for FACS analyses (left panel) and mitochondrial membrane potential ΔΨm (right panel). F, Overexpression of KIF1Bβ in the absence of YME1L1 does not alter long forms of OPA1. The cells used in (E) were subjected to Western blot analysis. C, cytoplasm; FACS, fluorescence‐activated cell sorting; L, long‐form OPA1; M, mitochondria; S, short form OPA1 [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
