Figure 4.
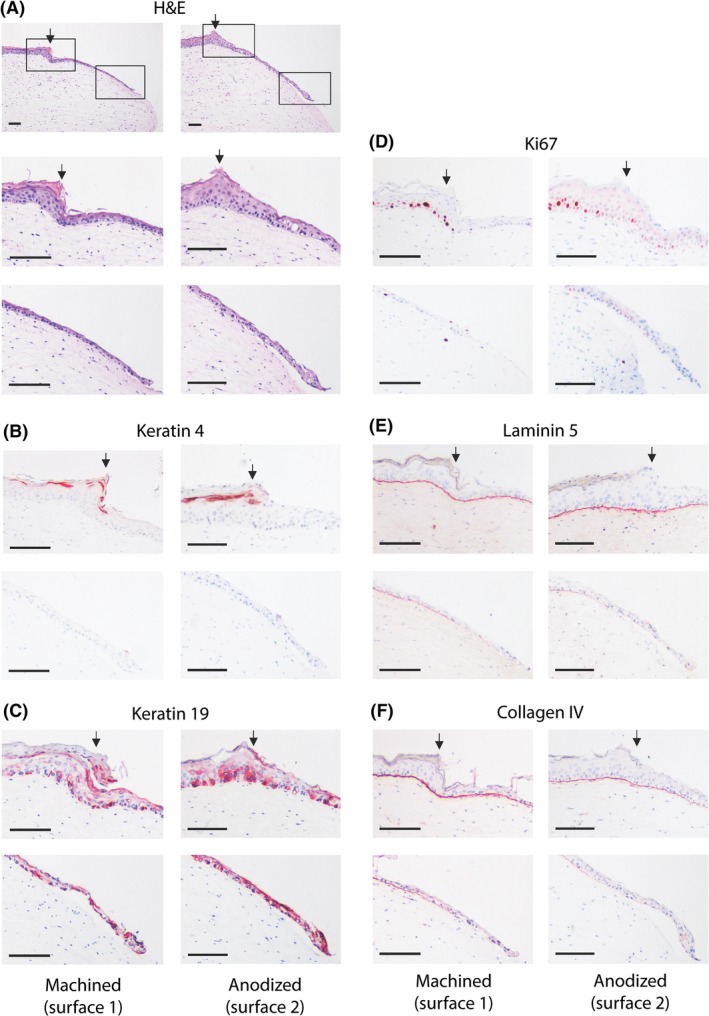
Immunohistochemical analysis of down‐growing reconstructed human gingiva (RHG) epithelium adjacent to the abutment surface. A, Tissue sections (5 μm) were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) to visualize the histology. A stratified and cornified gingiva epithelium is observed in the RHG in the area that was not in contact with the abutment surface (to the left of the arrow). Down‐growing epithelium can be observed to the right of the arrow. The solid box left represents the upper panels following staining, and shows the transition of the epithelium phenotype as it comes into contact with the abutment surface. The solid box right represents the lower panels following staining, and shows the migrating front of the junctional epithelium adjacent to the abutment surface. B‐F, Immunohistochemistry using antibodies directed against epithelial biomarkers (keratin 4 [K4] or keratin 19 [K19]), proliferation marker Ki67, or basement membrane proteins collagen IV and laminin 5 (red immune‐staining). Scale bar = 100 μm. Representative results obtained from 12 images and 3 independent experiments are shown; see Materials and Methods, section Data Analysis for further information
