Figure 2.
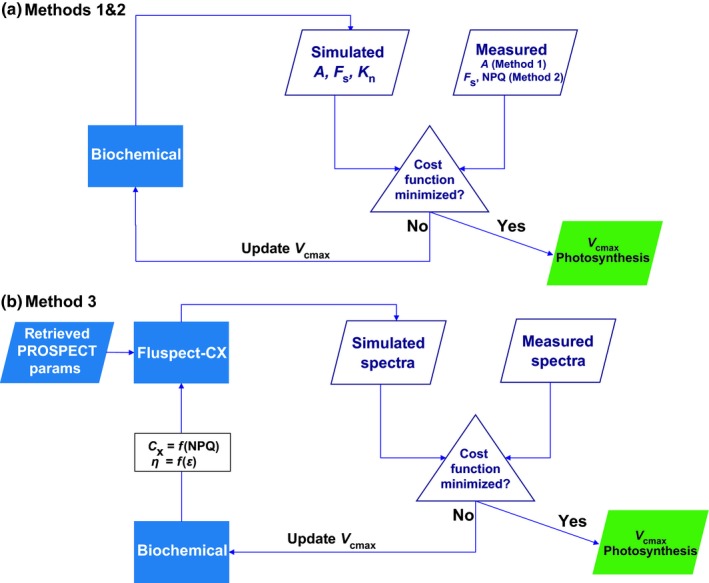
The schematics for three methods of V cmax retrieval. (a) In methods 1 and 2, the biochemical model is inverted by constraining the inversion with either the assimilation rate A curves (method 1) or with nonphotochemical quenching (NPQ) and steady‐state fluorescence F s curves (method 2). (b) In method 3, the combined model is inverted. First, the prospect parameters (see Table 1) are retrieved once per leaf. Next, the biochemical model is initialized with standard input values. Parameters for photochemical reflectance C x and fluorescence quantum efficiency η are prescribed as functions of NPQ and fluorescence emission efficiency ε, following Eqns 9 and 10, respectively. C x and η, together with the estimated prospect parameters, are provided as inputs of fluspect. The difference between the fluspect simulation and measured spectra is minimized by a cost function, resulting in the optimization of the chosen parameters.
