Figure 2 |. Crystal structure of sKLB bound to FGF21CT reveal two distinct binding sites.
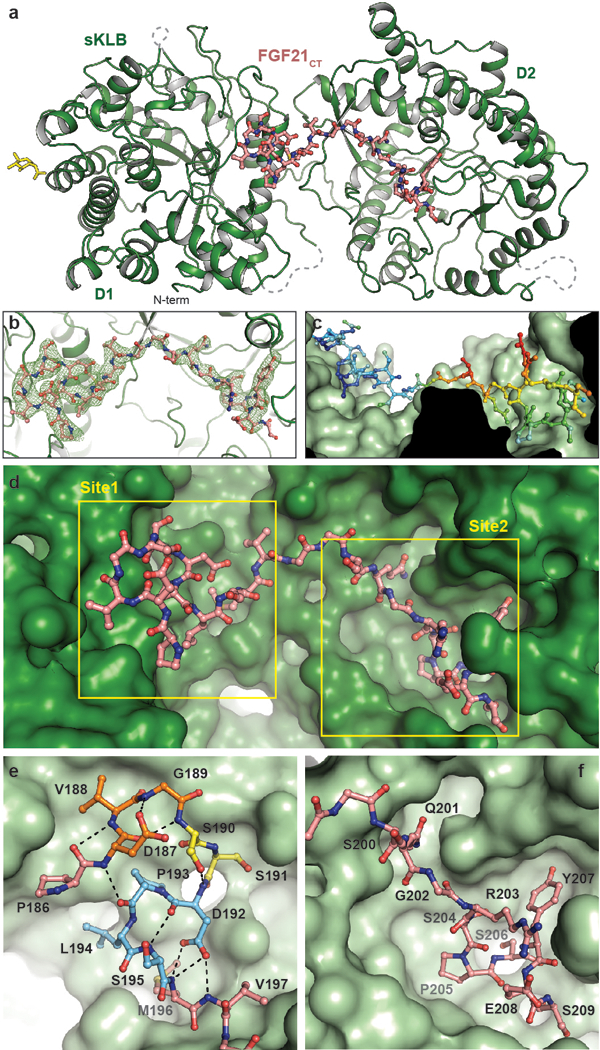
a, The structure of sKLB (green) in complex with FGF21CT (salmon) is shown as ribbon and ball-and-stick representation. N-linked glycans are shown as yellow sticks. Nb914 is omitted for clarity. Regions that do not exhibit significant electron densities are shown as grey dashed lines. b, FGF21CT binding site showing |Fo|-|Fc| omit map contoured at 3.0 σ for FGF21CT. c, Surface of sKLB interacting with FGF21CT are color-coded according to the B-factor values, ranging from 52.76 Å2 (blue) to 103.63 Å2 (red). d, Surface representation of sKLB (green) highlighting two binding sites, site 1 and site 2 of FGF21CT (salmon, ball-and-stick). e, Site 1 forms a series of internal hydrogen bonds (black dashed lines) through three consecutive turns (orange, yellow, and light blue), creating a structural element that binds to D1 of sKLB. f, Site 2 interacts with pseudo-substrate binding region of D2 of sKLB.
