Figure 3 |. Comparison of β-glucosidase and β-Klotho structures; evolution of a sugar cutting enzyme into a receptor for endocrine FGF.
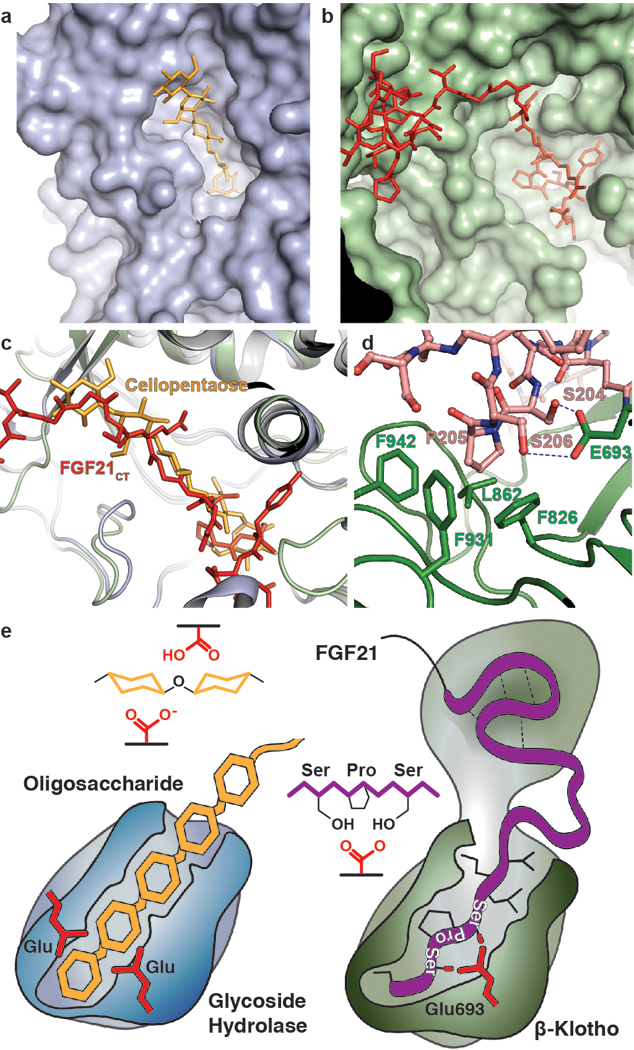
a, b, The structure of (a) rice β-glucosidase (light blue, surface presentation) in complex with cellopentaose (orange, stick presentation) (PDB: 3F5K) and (b) site 2 of sKLB (pale green, surface presentation) in complex with FGF21CT (red, stick representation). Cellopentaose binds to the active site of β-glucosidase and FGF21CT binds to the corresponding pseudo-substrate binding site of β-Klotho. c, Superimposition of the structures of cellopentaose-bound rice β-glucosidase and FGF21CT-bound sKLB. d, E693 of β-Klotho makes contacts with S-P-S motif of FGF21 via interaction with hydroxyl moieties of serines mimicking sugar hydroxyls in their interaction with glutamates in the catalytic site of β-glucosidase. e, Schematic diagram comparing the substrate-binding pocket including the two glutamates required for glycoside hydrolase activity and the ligand-binding pocket of β-Klotho depicting interactions between E693 with the S-P-S motif.
