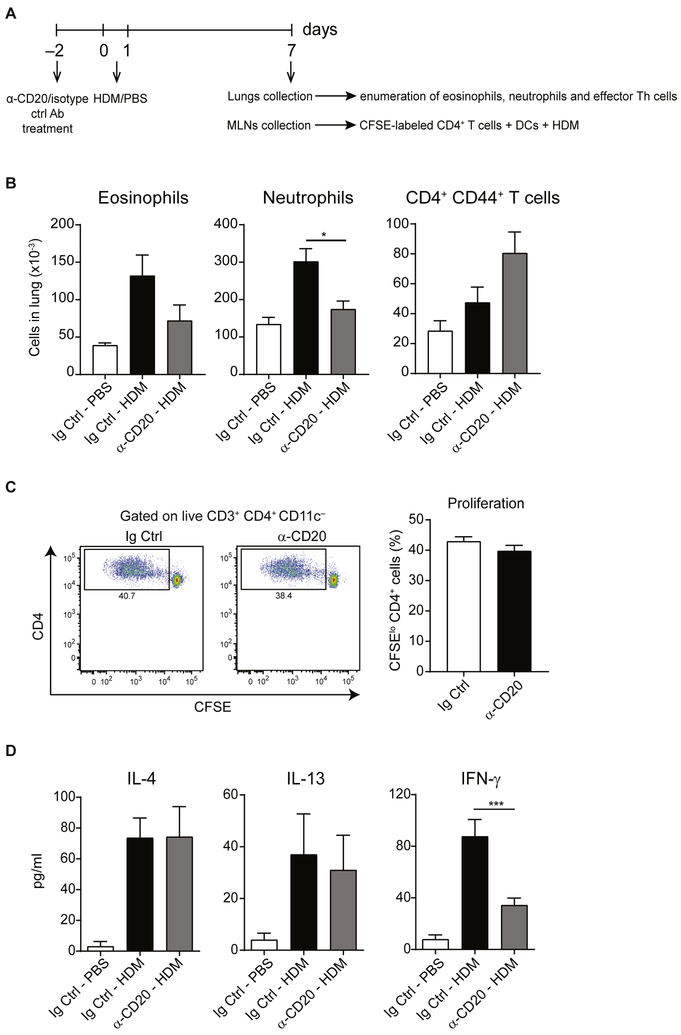
FIG 7.
Depletion of B cells before priming with HDM results in reduced numbers of eosinophils and neutrophils in the lungs but does not influence the capacity of MLN TH cells to secrete IL-4 or IL-13. A, Experimental set-up of the experiment. C57BL/6 mice were treated with α-CD20 or isotype control antibody (Ig Ctrl) on day −2, treated with HDM or PBS intranasally on days 0 and 1, and analyzed on day 7. Lungs were collected, and numbers of eosinophils, neutrophils, and effector TH cells were evaluated. Additionally, CD4+ T cells were isolated from MLNs, labeled with CFSE, and cocultured with MLN DCs in the presence of HDM for 4 days. B, Enumeration of eosinophils, neutrophils, and effector TH cells in lung tissue. C, Proliferation, as assessed by means of CFSE dilution, was measured by using flow cytometry. Representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) plots and cumulative data from 4 mice per group. D, Supernatants from cocultures were collected on day 4, and cytokine levels were measured by means of ELISA. IL-5, IL-17, and IL-21 levels were less than the limit of detection. Data are representative (Fig 7, B and C) or pooled (Fig 7, C) from 2 (Fig 7, B) or 4 (Fig 7, C and D) independent experiments. Graphs show the mean ± SEM. *P < .05 and ***P < .001.