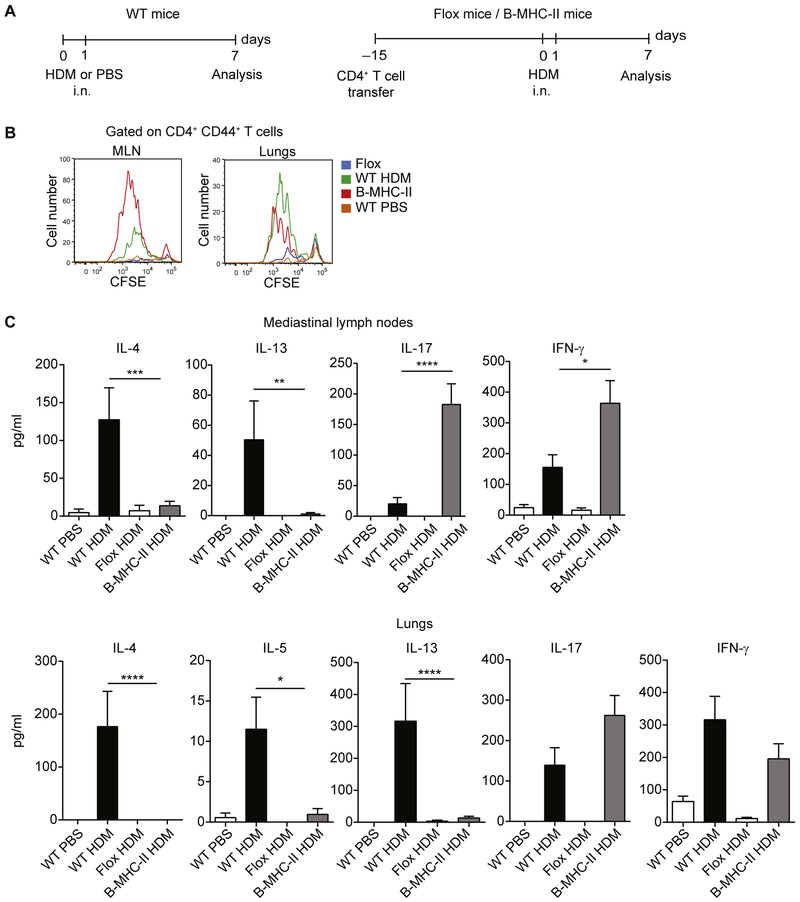
FIG 8.
B cells are able to prime CD4+ T cells in response to HDM. A, Experimental set-up. WT C57BL/6 mice were sensitized with HDM or treated with PBS on days 0 and 1 and analyzed on day 7 (left). B-MHC-II and Flox mice (both on C57BL/6 background) received intravenous injection of 107 polyclonal CD4+ T cells from WT C57BL/6 mice before HDM sensitization to reconstitute the CD4+ T-cell compartment. Mice were subsequently sensitized with HDM on days 0 and 1 and analyzed on day 7 (right), i.n., Intranasal. B, MLNs or lung CD4+ T cells were labeled with CFSE and cocultured with MLN DCs in the presence of HDM for 4 days. Proliferation was assessed by means of CFSE dilution. C, Cytokine concentrations in the day 4 culture supernatants were measured by using ELISA. IL-21 levels in both data sets and IL-5 levels in the MLN data set were less than the limit of detection. Data are representative (Fig 8, B) or pooled (Fig 8, C) from 3 independent experiments. Graphs show the mean ± SEM. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, and ****P < .0001.