Figure 1.
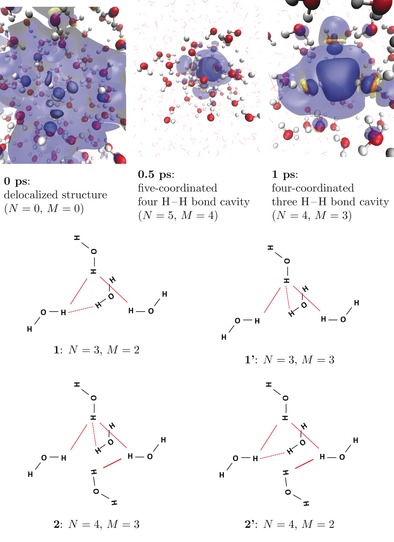
Dynamic structure of the hydrated electron: N is the number of H−H bonds; M is the maximum number of H−H bonds formed by one atom. The number of water molecules forming the cavity is almost everywhere equal to N+1. Top: evolution of the hydrated electron's spin density exhibits rapid cavity formation. Blue: positive spin density; yellow: negative spin density. Spin density isovalues: opaque: ±0.0015 a.u.; transparent: ±0.0001. Bottom: Typical structures of the hydrated electron's cavity with bonding schemes: structures 1 and 1′, 2 and 2′ are isomeric.
