Figure 2.
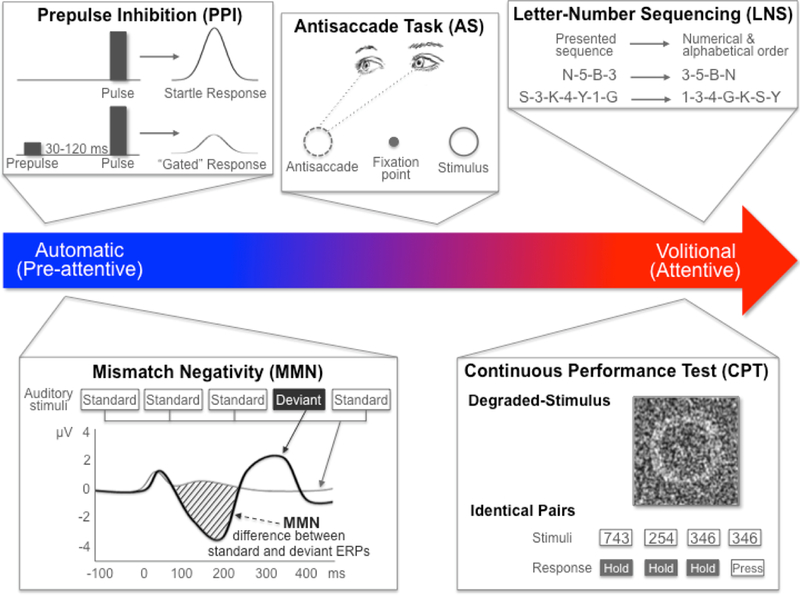
The range of SZ-related endophenotypes from automatic to volitional. PPI and MMN are neurophysiological endophenotypes representing automatic, or preattentive, processes that can be elicited with no active participation from the test subject. PPI is measured as the percent inhibition (i.e., gating) of the startle reflex in response to a weak prestimulus. MMN is measured as the difference between the waveforms for a standard stimulus ERP and a deviant stimulus ERP. Neurocognitive endophenotypes like CPT and LNS are volitional, or attentive, and require active participation from the subject. CPT measures sustained attention as the signal/noise discrimination ratio (d’) of blurred target stimuli (in the DS-CPT) or pairs of identically presented stimuli (in the CPT-IP). LNS measures working memory as the correct reordering of a verbally presented list of intermixed numbers and letters. AS is measured as the ratio of correct antisaccades (i.e., looking in the opposite direction of the presented stimulus) to total interpretable saccades (i.e., eye movements in any direction). Although AS is a neurophysiological measure, subjects are required to actively participate and control their response. AS: antisaccade; CPT: continuous performance test; DS: degraded stimulus; ERP: event-related potential; IP: identical pairs; LNS: letter-number sequencing; MMN: mismatch negativity; PPI: prepulse inhibition; SZ: schizophrenia.
