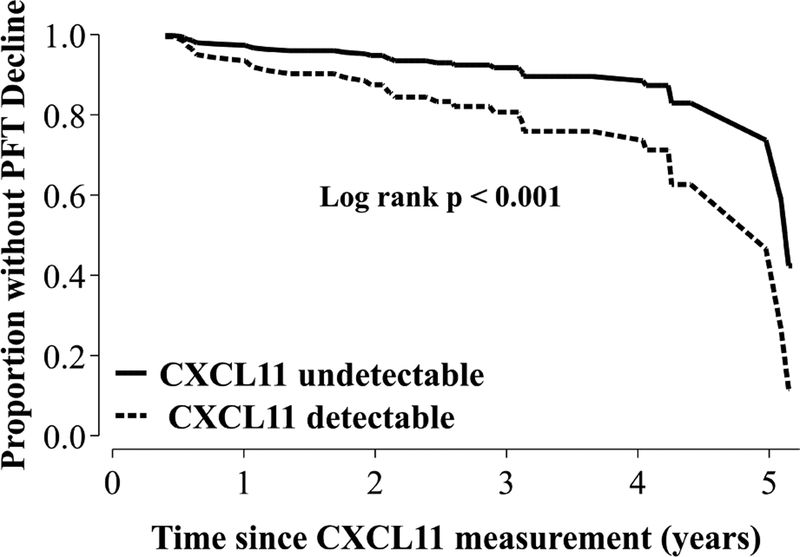
Fig. 5.
Relationship between serum CXCL11 measurement and longitudinal decline in lung function.
Thirty-three subjects were identified who experienced a decline in absolute FVC or DLCO of 10% or 15%, respectively, over the study period (5 years). Total time at risk for all subjects analyzed was 226 person-years. We used a Cox proportional hazard modeling that adjusted for age, race, sex, immunosuppression use, and initial radiographic burden of lung involvement as assessed by chest x-ray “Scadding Stage” to determine a hazard ratio for CXCL11. We also dichotomized subjects based on whether they had a CXCL11 level that was undetectable (<62.5 pg/mL, N = 37) or detectable (>62.5 pg/mL, N = 48). Using this dichotomous designation, the adjusted log rank p-value was <0.001 and the HR was also statically significant (hazard ratio 2.5, 95% CI 1.1 – 5.7 p = 0.027). Data are displayed as adjusted survival curves for detectable versus undetectable CXCL11 levels. Abbreviations: DLCO = Diffusing Capacity for Carbon Monoxide, FVC = Forced Vital Capacity, HR = hazard ratio.