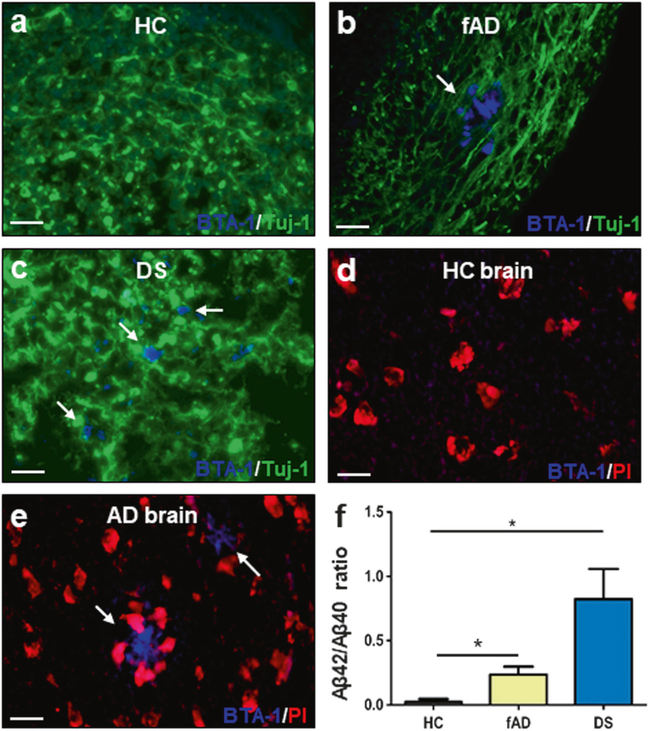
Fig. 4.
Characterization of Aβ deposition by staining with an amyloid-binding dye and by biochemical studies of insoluble Aβ. a–c COs prepared from iPSCs derived from familiar Alzheimer’s disease (fAD), Down syndrome (DS) and healthy control (HC) patients were cultivated for 110 days. Amyloid deposits were stained with the BTA-1 dye (blue) and Tuj-1 (green). d, e Staining of Aβ plaques with the BTA-1 dye (blue) and propidium iodide (PI, red) in brain slides from HC and AD patients. Scale bars in panels a–e: 25 μm. f ELISA assay measuring the levels of total insoluble Aβ peptide (Aβ40 and Aβ42) in COs homogenates. Protein concentration in the COs homogenates was measured by BCA and equal amounts of total protein were used. Extraction was done with formic acid as described in Methods. The figure shows the ratio Aβ42/Aβ40 in the insoluble fraction. Each value corresponds to the average ± SEM of six replicates. For this analysis, 80–220 organoids were used for each replicate. Data was analyzed by one-way ANOVA, and unpaired Student’s t-test. *P <0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001