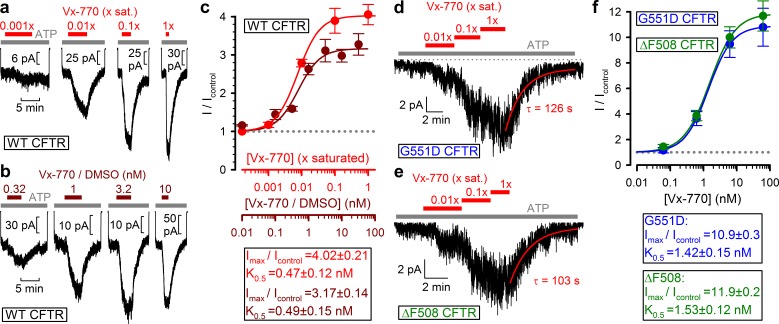
Figure 3. Vx-770 stimulates CFTR currents already at subnanomolar concentrations.
(a-b) Macroscopic WT CFTR currents elicited by 2 mM ATP are reversibly stimulated by exposure (red and brown bars) to indicated concentrations of Vx-770, diluted either from a 1x saturated aqueous stock (a) or from a 10-mM stock dissolved in DMSO (b). (c) Fractional stimulation of WT CFTR currents by Vx-770 diluted from a 1x saturated aqueous (red symbols and abscissa), or a DMSO-based (brown symbols and abscissa), stock. Abscissae are aligned based on the aqueous solubility of Vx-770 (~62 nM). (d–e) Quasi-macroscopic currents of prephosphorylated G551D (d) and ΔF508 (e) CFTR channels in 2 mM ATP are reversibly stimulated by exposure (red bars) to indicated concentrations of Vx-770, diluted from a 1x saturated aqueous stock. Deactivation time courses following drug removal are fitted with single exponentials (red lines). (f) Fractional stimulation of G551D (blue symbols) and ΔF508 (green symbols) CFTR currents by Vx-770 diluted from a 1x saturated aqueous stock; abscissa has been calibrated. Symbols in (c) and (f) show mean ± S.E.M. from 3-13 experiments, solid curves are fits to an adapted Hill equation (Materials and methods) with parameters plotted. Hill coefficients were 1.31±0.65 and 1.32±0.47 for WT in Vx-770 or Vx-770/DMSO, 1.12±0.07 for ΔF508, and 1.22±0.10 for G551D CFTR.