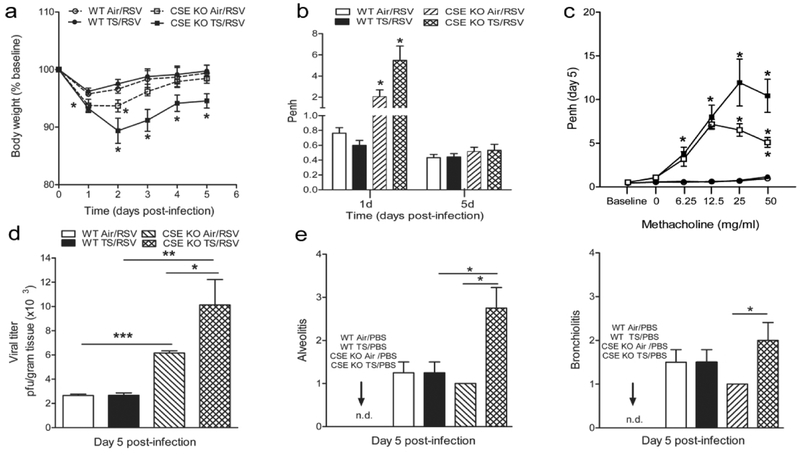
Figure 2.
TS and CSE gene deficiency exacerbate clinical disease, viral replication, and AHR following RSV infection. Groups of CSE KO and WT mice were exposed to TS or Air as in Fig. 1, followed by infection with RSV as described in Material and Methods. (a) Effect of TS exposure on RSV induced disease. Change in body weight was measured over a period of 5 days after infection. (b) Airway obstruction represented by baseline Penh at day 1 and 5 after RSV infection. (c) AHR in response to MCh challenge at day 5 after RSV infection. (d) Increased RSV replication in the lung of TS /CSE KO mice, at day 5 after RSV infection lungs measured by plaque assay. (e) Lungs were harvested at day 5 after infection, fixed for slide preparation and H&E stained. Alveolitis and bronchiolitis inflammatory scores of prepared slides (scored as described in Materials and Methods). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4 mice (2 male and 2 female)/group and are representative of three independent experiments). *p<0.05.**p<0.01, ***p<0.001 CSE KO TS /RSV vs WT TS / RSV, CSE KO TS / RSV vs CSE KO Air/ RSV, CSE KO Air/RSV vs WT Air/RSV, WT TS / RSV vs WT Air/RSV.