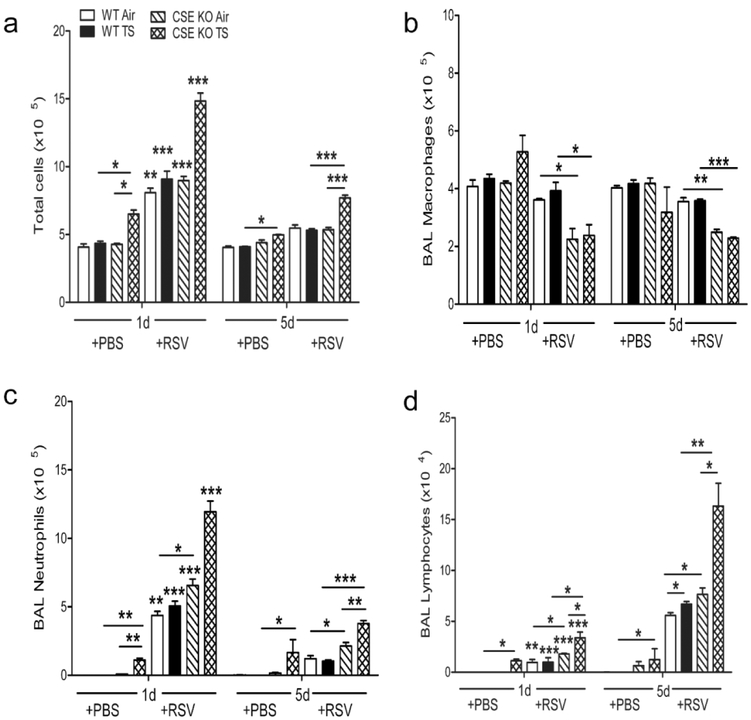
Figure 4.
TS and CSE deficiency increase airway inflammatory cells following infection. TS -or Air-exposed CSE KO and WT mice were infected with RSV or sham. BAL fluid was collected at different time points after infection and cell preparations were stained (Hema 3 stain, Fisher Scientific) and counted under the microscope (200 cells/slide). TS increased the influx of total cells (a), macrophages (b), neutrophils (c), and lymphocyte (d) into the BAL of CSE KO PBS mice, which was further exacerbated in the RSV infected CSE KO mice, compared with WT animals. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4 mice (2 male and 2 female)/group and are representative of three independent experiments). *p<0.05.**p<0.01, ***p<0.001 CSE KO TS/RSV vs WT TS / RSV, CSE KO TS / RSV vs CSE KO Air/ RSV, CSE KO Air/RSV vs WT Air/RSV, WT TS / RSV vs WT Air/RSV, CSE KO TS / PBS vs. WT TS / PBS, and CSE KO TS /PBS vs. CSE KO Air/PBS, WT Air/RSV day 1pi vs. WT Air/RSV day 5pi, WT TS/RSV day 1pi vs. WT TS/RSV day 5pi, CSE KO Air/RSV day 1pi vs. CSE KO Air/RSV day 5pi, CSE KO TS/RSV day 1pi vs. CSE KO TS/RSV day 5pi.