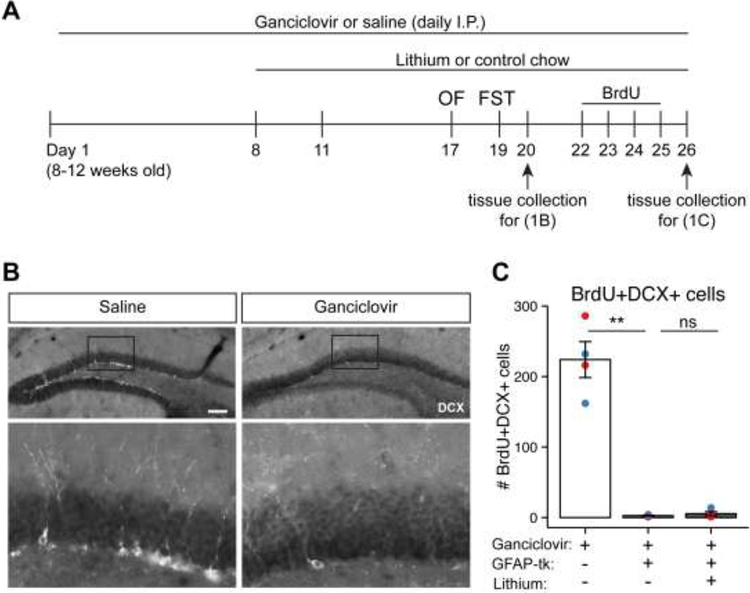
Figure 1.
Intraperitoneal ganciclovir ablates adult hippocampal neurogenesis.
A) Experiment schedule for quantification of NPC ablation.
B) Fluorescent immunohistochemistry for DCX, a marker of immature neurons that derive from GFAP-positive NPCs [15], in brains collected one day after the FST. Daily ganciclovir depletes DCX-positive NPC progeny in the dentate gyrus, indicating ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis. Scale bar: 100um.
C) Quantification of NPC ablation from mice treated with BrdU (after completing behavior testing). BrdU+ DCX+ double-positive cells in the SGZ are depleted in GFAP-TK mice compared to wild-type. Lithium treatment does not change the extent of NPC ablation. Bar graph and error bars represent mean ± SEM; n = 4 per group. Individual data points are color-coded by sex (red = male, blue = female). Significance: ** p < 0.005 by Welch’s two sample t-test. OF, Open Field; FST, Forced Swim Test; I.P., intraperitoneal; DCX, Doublecortin.