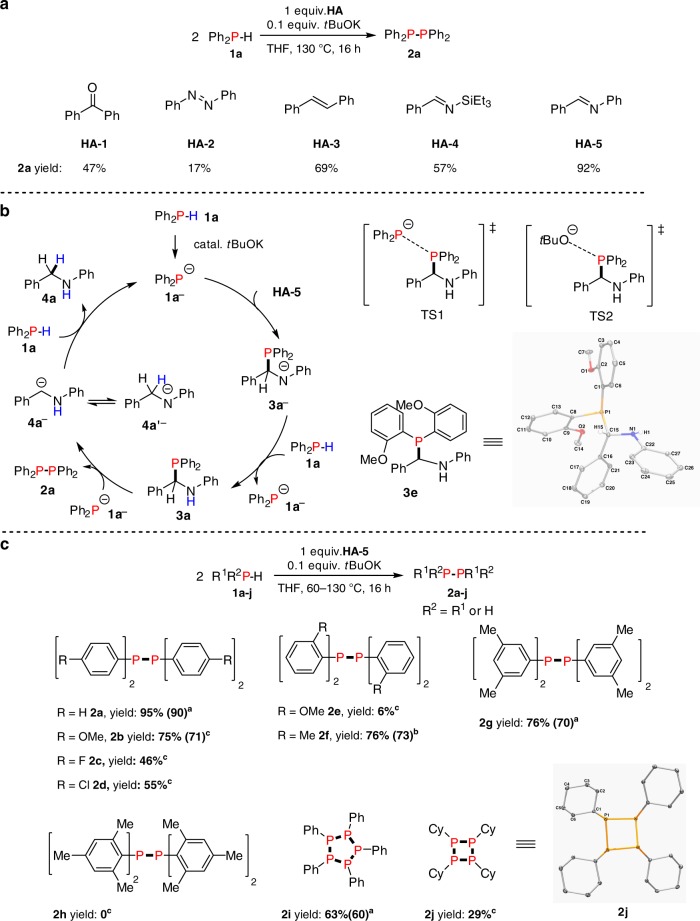
Fig. 2.
tBuOK-catalysed dehydrocoupling of phosphines in the presence of HA. a The effect of selected HA in the homodehydrocoupling of Ph2PH. b Proposed reaction mechanism via 3a as key intermediate and SN2-type reaction to produce 2a, K+ ions are removed from the catalytic cycles for clarity. Proposed transition state structures TS1, and TS2, for attack of 3a by incoming 1a− or tBuO−. X-ray crystal structure of hydrophosphination product 3e with non-hydrogen atoms shown as 30% probability ellipsoids. c, Reaction generality using different phosphines: reactions were performed with 0.1 mmol phosphines, 0.01 mmol tBuOK, 0.1 mmol HA-5, 0.5 mL THF in a J. Young NMR tube and yields were based on the phosphine as the limiting reagent and determined by 31P{1H} NMR spectroscopy using a capillary of PCl3 as a calibration standard, the numbers in brackets were isolated yields of products. a60 °C, b100 °C, c130 °C. X-ray crystal structure of 2j with non-hydrogen atoms shown as 30% probability ellipsoids