Fig. 4.
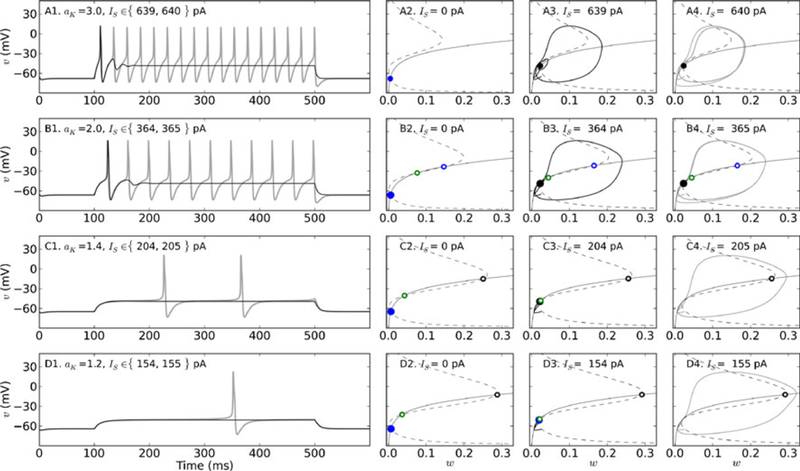
Transitions from rest to repetitive spiking for different levels of Shab channel expression. Membrane potential dynamics, nullclines, and trajectories in phase space for aK = 3.0 (A1–A4), 2.0 (B1–B4), 1.4 (C1-C4)), or 1.2 (D1-D4). A1, B1, C1, D1: Responses to two 400 ms square pulses of current, the first at 1 pA below (black traces) and the second at Icyc (gray traces). A2, B2, C2, D2: Nullclines Icyc for υ (dashed) and w (solid) are plotted in phase space in the absence of stimulation (Is = 0). Intersections of the nullclines are marked with circles to indicate stable (filled) or unstable (open) fixed points. Nodes are blue, saddle points are green, and foci are black. If there is more the one fixed point, the one located at the lowest membrane potential has the larger marker size. A3, B3, C3, D3: Nullclines and trajectories (solid black) of the system in phase space corresponding to the response to current stimulation 1 pA below Icyc. Nullclines and fixed points are plotted as described above. A4, B4, C4, D4: Nullclines and trajectories of the system in phase space corresponding to the response to current stimulation at Icyc. Parameters: σw = 0.7,. τ̄w = 10 ms, with initial conditions (w0, υ0) = (0.025, −65). See Table 1 for all other parameters
