Figure 5. H4K16 was required for ovarian germline stem cell (GSC) maintenance and male viability.
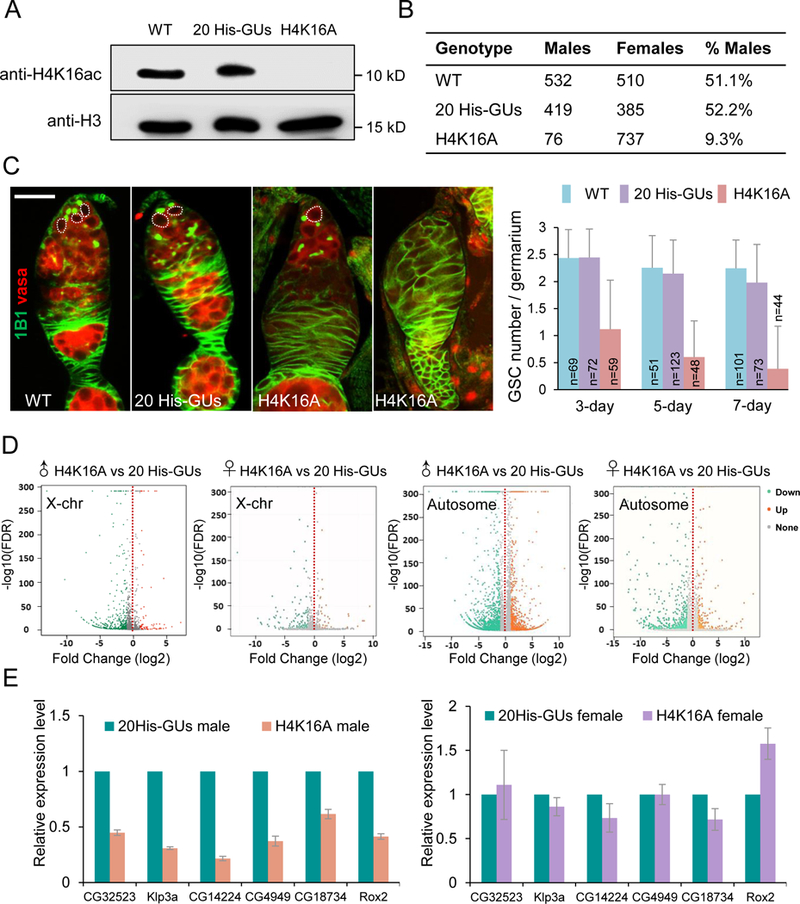
(A) Western blot of adult fly extract from wild type (WT; w1118), 20 His-GUs (20 copies of wild-type histone gene units), and H4K16A genotypes.
(B) The number of male and female progeny from wild type, 20 His-GUs and H4K16A parents.
(C) Confocal images of ovaries from w1118, 20 His-GUs and H4K16A flies. GSCs (dotted line) stained with 1B1 (green) and Vasa (red). Histogram shows the number of GSCs per germarium at days 3, 5, and 7 adulthood. The number of germaria examined per genotype is shown on each column. Values are means ± SEM. Scale bar: 20 µm.
(D) Transcriptome comparisons of third larvae salary glands between H4K16A mutants and 20His-GUs.
(E) RT-PCR verification of effects of H4K16A mutation. Six-linked genes (CG32523, Klp3a, CG14224, CG4949, CG18734, and Rox2) were chosen as the targets. Values are means ± SEM of three biological replicates (rp49 was the reference gene for normalization, RNA was extracted from salivary gland).
See also Figure S6.
