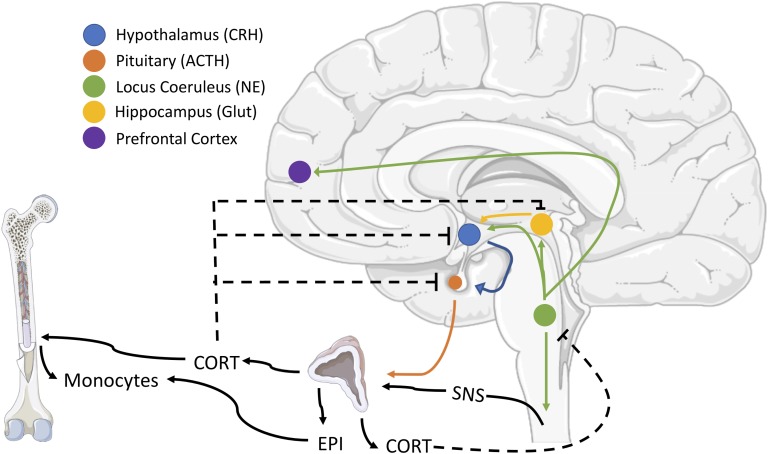
Figure 4.
Schematic of the effects of peripheral glucocorticoids and catecholamines on peripheral monocytes and feedback on locus coeruleus neurons. Brainstem noradrenergic neurons contribute to the activation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and activation of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), which results in the collective release of circulating corticosterone or cortisol (CORT) and epinephrine (EPI), respectively. CORT causes monocytes to leave the bone marrow, whereas EPI primes their responses to future activation. CORT provides negative feedback at multiple levels of HPA regulation and inhibits central noradrenergic release. Negative feedback is indicated by dashed lines. CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; Glut, glutamate.