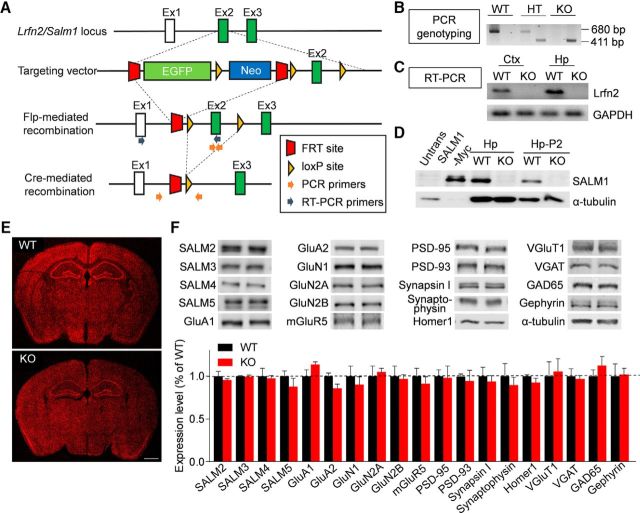
Figure 1.
Generation and characterization of Lrfn2−/− mice. A, Strategy for the generation of Lrfn2−/− mice. B, PCR genotyping of Lrfn2−/− mice. HT, Heterozygous; C, Confirmation of Lrfn2 exon 2 deletion by qRT-PCR analysis of whole-brain mRNAs (P31). D, Lack of LRFN2 protein expression in the Lrfn2−/− brain (P21), as determined by immunoblot analysis of hippocampal lysates: total (Hp) and crude synaptosomal (Hp-P2). Untrans, Untransfected HEK293 cell lysates; SALM1-Myc, lysates of HEK293 cells transfected with SALM1-Myc. E, Normal gross morphology of the Lrfn2−/− brain (P28), as shown by staining for NeuN (a neuronal marker). Scale bar, 1 mm. F, Normal levels of other SALMs (SALM2-5), glutamate receptor subunits [AMPA (GluA1/A2), NMDA (GluN1/2A/2B), and metabotropic (mGluR5), and synaptic proteins (excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic and postsynaptic), compared with WT levels, as determined by immunoblot analyses of crude synaptosomal (P2) fractions from the WT and Lrfn2−/− hippocampus (P20–P23). Levels of the indicated proteins were normalized to those of α-tubulin for genotype comparisons. The dotted line indicates WT levels. n = 3 mice for WT and 4 mice for KO. NS, Student's t test (for additional details, see Figure 1-1).