Figure 6.
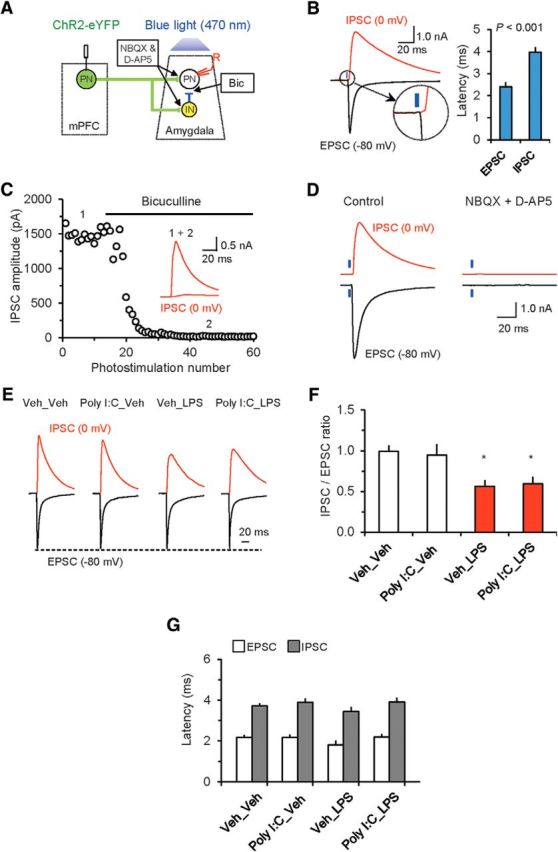
Feedforward inhibition in the mPFC–BLA pathway is diminished in postnatally immunoactivated mice. A, Experimental design for analyzing neural circuits of feedforward inhibition in the mPFC–BLA projections. Glutamatergic inputs to both BLA PNs and INs, activated by blue light stimulation of mPFC fibers, were blocked by AMPA and NMDA receptor antagonists (10 μm NBQX and 50 μm D-AP5, respectively). Projections from IN to PN were suppressed by the GABAA receptor antagonist bicuculline (Bic, 30 μm). B, Left, Synaptic responses were induced by photostimualtion (7.4–10.2 mW/mm2) and recorded in BLA neurons at −80 mV (black trace, EPSC) and 0 mV (red trace, IPSC). The inset shows a delayed onset (synaptic latency) of synaptic currents recorded at 0 mV. Right, mean synaptic latencies of IPSCs and EPSCs. The IPSC latency (at a holding potential of 0 mV) was much longer compared with EPSCs recorded in the same neurons at a holding potential of −80 mV, suggesting that the IPSC is polysynaptic in nature (n = 10 neurons from 3 mice). C, IPSCs at a holding potential of 0 mV were completely blocked by the GABAA receptor antagonist bicuculline (30 μm). D, Both EPSCs and IPSCs (recorded in BLA PNs at −80 or 0 mV, respectively) were completely blocked by NBQX (10 μm) and D-AP5 (50 μm), confirming that the IPSCs, mediated by activation of local circuit INs, are polysynaptic in origin and triggered by glutamatergic mPFC inputs to IN. E, EPSCs and IPSCs (averages of 10 traces) recorded in the same neurons in slices from all experimental groups. IPSCs were normalized to the mean amplitude of the EPSC at a holding potential of −80 mV to allow the comparison of changes in the IPSC amplitude between the groups. F, The IPSC/EPSC amplitude ratio was decreased in Veh_LPS and Poly I:C_LPS groups, indicating an effect of PIA on the balance between excitation and inhibition in mPFC–BLA projections (Veh_Veh group: n = 17 neurons from 7 mice; Poly I:C_Veh: n = 18 neurons from 9 mice; Veh_LPS: n = 13 neurons from 5 mice; Poly I:C_LPS: n = 23 neurons from 11 mice). G, Immunoactivation had no effect on the latencies of EPSCs or IPSCs in mPFC–BLA projections (Veh_Veh group: n = 17 neurons from 7 mice; Poly I:C_Veh: n = 18 neurons from 9 mice; Veh_LPS: n = 13 neurons from 5 mice; Poly I:C_LPS: n = 23 neurons from 11 mice). *p < 0.05.
