Figure 7.
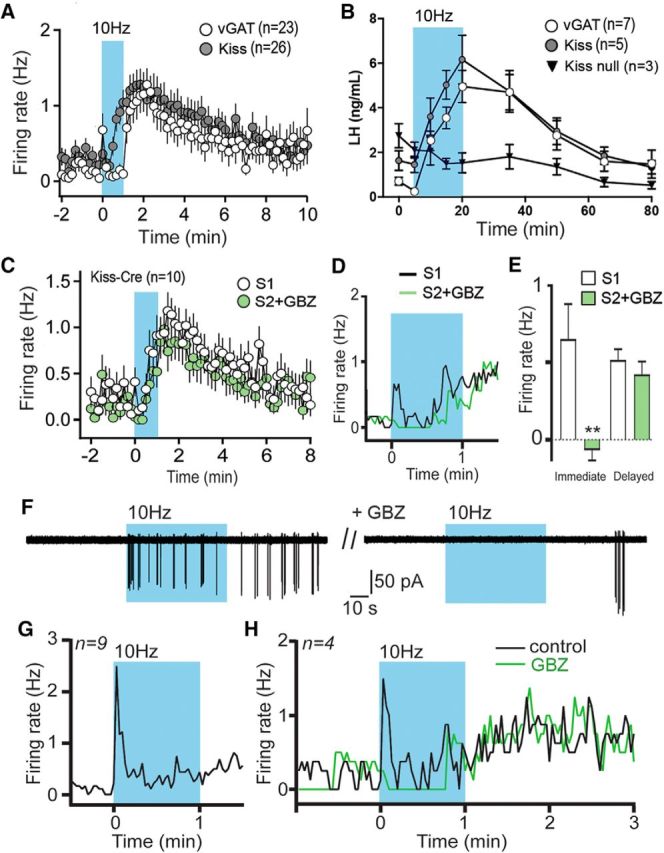
GABA-kisspeptin cotransmission in the regulation of GnRH neuron firing and LH secretion. A, Superimposition of GnRH neuron firing responses to optogenetic activation (600 pulses at 10 Hz) of RP3VGABA neuron (white circles) or RP3VKISS neuron (gray circles) axons. B, Time course of LH secretion in response to 15 min, 10 Hz optogenetic activation of RP3VGABA neurons (from Fig. 5D), RP3VKISS neurons (from Fig. 5A), and RP3VKISS neurons in which kisspeptin has been deleted (kiss-null). C, Two successive optogenetic activations (600 pulses at 10 Hz) of RP3VKISS neuron axons were delivered at 15 min intervals, with the second stimulus delivered in the presence of gabazine (GBZ; 5 μm) in the bath. D, Expanded view of the 1 min optogenetic stimulation period showing the suppression of immediate mean GnRH neuron firing by GBZ (green trace). E, The immediate response was abolished by GBZ, whereas the delayed response was unaffected (**p < 0.01). F, The immediate response of a GnRH neuron to a blue-light stimulation train (600 pulses at 10 Hz) is abolished in the presence of GBZ. G, Time course showing the mean firing rates of 9 GnRH neurons that exhibited immediate responses to blue-light stimulation in AAV-injected Kiss1-IRES-Cre mice. H, In a further four GnRH neurons displaying this immediate response following 10 Hz blue light stimulation of RP3VKISS neuron axons (black line), treatment with GBZ (green line) abolished the immediate increase in firing but had no effect on the delayed increase observed after the stimulation.
