Figure 4.
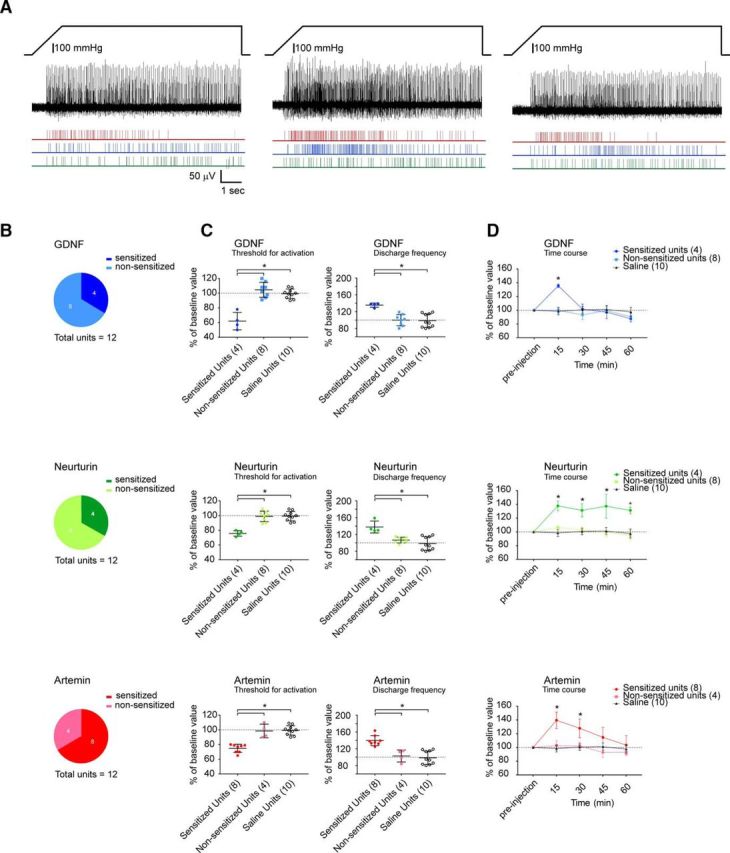
GDNF, neurturin, and artemin applied directly to the marrow cavity sensitizes mechanically activated bone afferent neurons. A, Example of a whole-nerve recording and rasters of single-unit activity in response to a 300 mmHg ramp-and-hold pressure stimulus before (left), and 15 min (middle) and 30 min (right) after the application of artemin to the marrow cavity. There was a clear reduction in threshold for activation and an increase in discharge frequency in single units isolated from this recording after the application of artemin. B, Pie charts representing the proportion of units that were sensitized by each of the GFLs. Sensitization was defined as a 20% increase in discharge frequency, as outlined in Materials and Methods. GDNF and neurturin each sensitized 4 of 12 single units tested (n = 5 animals; N = 4 of 12 units), and artemin sensitized 8 of 12 units tested (n = 4 animals; N = 8 of 12 units). C, Threshold for activation (left panels) and the discharge frequency (right panels) of single mechanically activated units expressed as a percentage of preinjection values at 15 min after the injection of each GFL (n = 12 units for each) or saline (n = 4 animals; N = 10 units). At 15 min, the threshold for activation was significantly decreased and discharge frequency was significantly increased in GDNF-, neurturin-, or artemin-sensitized units, relative to nonsensitized units and the saline control (Bonferroni's post hoc test, *p < 0.05). D, Time course of GFL-induced sensitization. GDNF-sensitized units had significantly increased discharge frequency only at 15 min (Bonferroni's post hoc test, *p < 0.05), neurturin-sensitized units had significantly increased discharge frequency at each of the time-points tested (Bonferroni's post hoc test, *p < 0.05), and artemin-sensitized units had increased discharge frequency at 15 and 30 min (Bonferroni's post hoc test, *p < 0.05). Error bars in C and D represent the mean ± SEM.
