Figure 1.
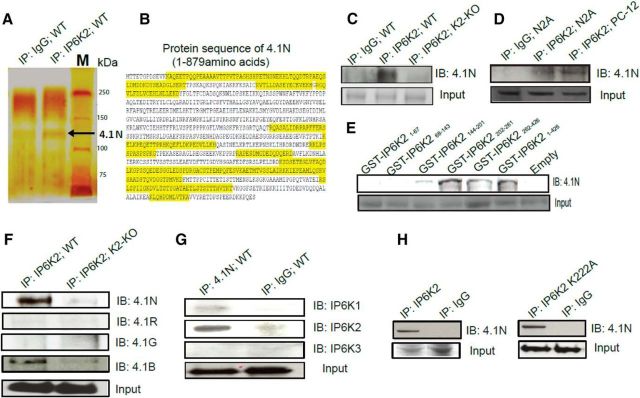
IP6K2 binds 4.1N in the brain. A, Silver staining of SDS-PAGE of IP6K2 immunoprecipitates (lane 2) from wild-type mouse brain lysate showed the presence of 4.1N protein (130 kDa) as a potential interacting partner of IP6K2 against IgG (lane1) as a control. B, Seventeen (17) 4.1N peptides (highlighted in yellow) were identified from IP6K2 immunoprecipitates using LC-MS/MS to confirm the identity of the 4.1N protein. C, Coimmunoprecipitates of IP6K2 from WT (lane 2) and IP6K2-knockout (K2-KO; lane 3) mouse brain lysates immunoblotted (IB) with 4.1N antibody confirmed the binding to 4.1N protein against IgG immunoprecipitate (IP) as a control (lane 1). D, Coimmunoprecipitates of IP6K2 blotted against 4.1N in neuronal cells also revealed its association with the 4.1N protein. Lane 1, IgG immunoprecipitate; lane 2, IP6K2 immunoprecipitates from N2A cell lysates; lane 3, IP6K2 immunoprecipitates from PC-12 cell lysates. E, GST-DNA constructs of different fragments of IP6K2 were transfected into N2A cells. Coimmunoprecipitates of such IP6K2 constructs expressing cell lysates were blotted against 4.1N antibody. This revealed the binding site of IP6K2 with 4.1N to be present between residues 202 and 261 of IP6K2. F, Coimmunoprecipitation of IP6K2 from wild-type mouse brain lysates (lane 1) and IP6K2-KO mice brain lysates (lane 2, control) showed the binding of 4.1N and 4.1B to IP6K2. However, 4.1G and 4.1R isoforms of the 4.1 family of proteins did not bind to IP6K2. G, Coimmunoprecipitates of 4.1N from mouse brain lysates were blotted against all three isoforms of IP6K (K1, K2, and K3). Corresponding immunoblots against IgG immunoprecipitates as a control (lane 2) showed selective binding of the 4.1N protein to IP6K2 and not to the IP6K1 or IP6K3 isoforms. H, Full-length IP6K2 and IP6K2 kinase dead mutants (K222A) were transfected into N2A cells. Immunoblots of the lysates from both cells showed confirmatory binding of 4.1N (lane 1) when compared with their IgG controls (lane 2) indicating that the binding of 4.1N to IP6K2 is not dependent on the kinase activity of the latter. Data are representative of three independent experiments performed under identical conditions. 4.1N peptides detected through LC/MS-MS with their respective peptide identification probability, mascot ion score and mascot identity score, Table 1-1.