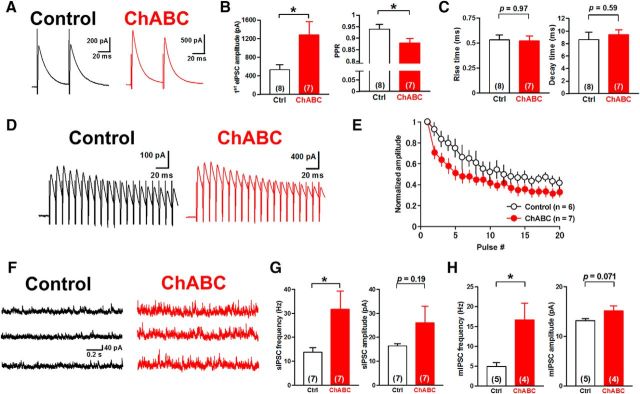
Figure 8.
Persistent effects of ChABC injected into the DCN in vivo on IPSCs. A, Representative traces of eIPSCs in neurons in the mouse DCN injected with control saline (left) and ChABC (right). Acute cerebellar slices were made 4–6 d after Ringer's solution or ChABC (10 U/ml) was injected into the interpositus nuclei of age P21 to P23 mice. B, Large DCN neurons of ChABC-injected mice showed an increase in the mean amplitude of first eIPSCs (left) and the reduction of the mean PPR (right) of eIPSCs. *p < 0.05 using unpaired Student's t test. C, No effect on the rise (left) or decay (right) kinetics of eIPSCs. D, Representative averaged eIPSCs induced by 20 stimuli at 100 Hz in large DCN neurons. E, Mean amplitudes of eIPSCs normalized to the first phasic eIPSC. ChABC injection enhanced the depression of eIPSCs. F, Representative traces of sIPSCs in large DCN neurons. ChABC treatment facilitated sIPSCs (right). G, Mean frequency (left) and amplitude (right) of sIPSCs. ChABC increased the frequency of sIPSC significantly. *p < 0.05 using unpaired Student's t test. H, Mean frequency (left) and amplitude (right) of mIPSCs. ChABC injection in vivo increased the mean frequency but not the mean amplitude of mIPSCs. *p < 0.05 using unpaired Student's t test. Ctrl, Control.