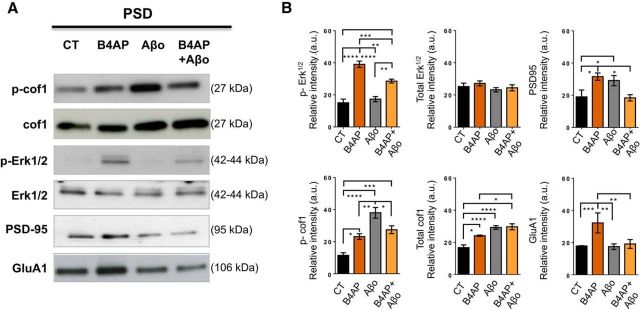
Figure 3.
Aβo induces phosphorylation of cof1 and blocks cLTP in primary cortical neurons. A, Representative Western blots of PSD-enriched fraction of synaptosomes harvested from primary cortical neurons (DIV 14) exposed to cLTP in the presence or absence of Aβo (15 min pretreatment, 100 nm). B, Relative quantification of Western blots in A demonstrated robust increases in phospho-Erk1/2, GluA1, and PSD-95 induced by cLTP and blocked by pretreatment with Aβo. Aβo by itself caused an increase in cof1 and p-cof1 at the PSD. Two-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc test with correction for multiple comparisons for data from n = 5–10 independent cultures per group revealed significant interactions for cLTP and Aβo as factors for phospho-ERK1/2, cof1, p-cof1, GluA1, and PSD-95. p-Erk cLTP, F(1,20) = 94.79, p < 0.0001; Aβo treatment, F(1,20) = 5.173, p = 0.0341; interaction, F(1,20) = 12.50, p = 0.0021; Erk cLTP, F(1,16) = 0.8026, p = 0.3836; Aβo treatment, F(1,16) = 1.814, p = 0.1968; interaction, F(1,16) = 0.04813, p = 0.8291; PSD-95 cLTP, F(1,23) = 1.105, p = 0.3242; Aβo treatment, F(1,23) = 0.118, p = 0.7343; interaction, F(1,23) = 21.13, p = 0.0001; p-cof1 cLTP, F(1,24) = 0.0563, p = 0.8144; Aβo treatment, F(1,24) = 41.05, p < 0.0001; interaction, F(1,24) = 21.41, p = 0.0001; cof1 cLTP, F(1,24) = 7.975, p = 0.0094; Aβo treatment, F(1,24) = 42.52, p < 0.0001; interaction, F(1,24) = 6.33, p = 0.0190; GluA1 cLTP, F(1,26) = 7.014, p = 0.0136; Aβo treatment, F(1,26) = 4.971, p = 0.0346; interaction, F(1,26) = 4.454, p = 0.0446; followed by Tukey's post hoc test with correction for multiple comparisons. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001. ****p < 0.0001.