Figure 7.
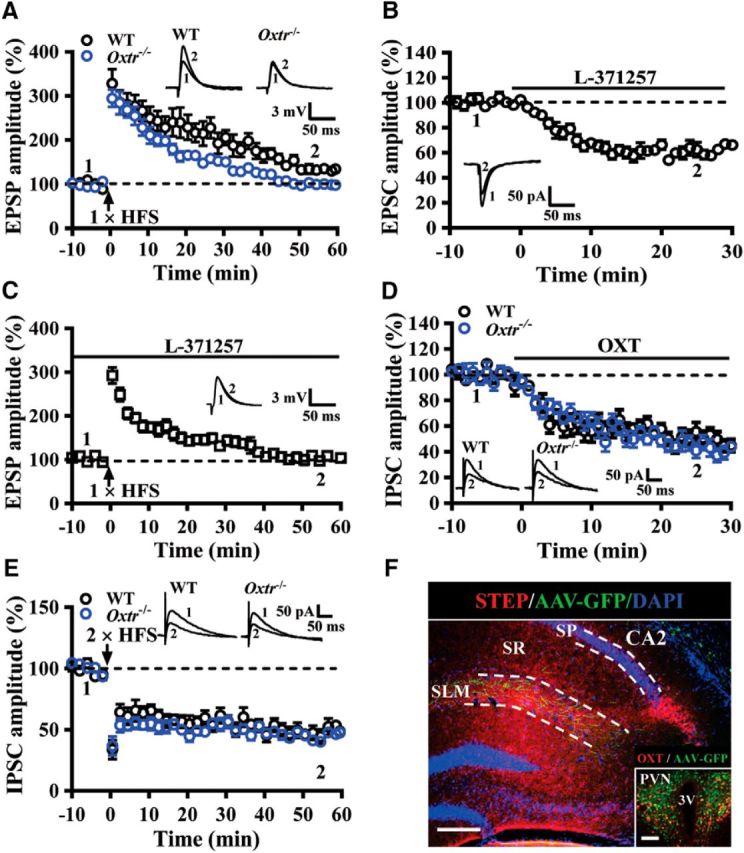
OXTRs are involved in regulating synaptic transmission and plasticity in the CA2. A, Summary of experiments showing one train of 1 s HFS at 100 Hz induced LTP of EPSPs at EC→CA2 synapses in slices from WT and Oxtr−/− mice. B, Summary of experiments showing effect of L-371257 (1 μm) on EPSC amplitude at EC→CA2 synapses in slices from naive mice. C, Summary of experiments showing effect of L-371257 (1 μm) on the induction of LTP by one train of 1 s HFS at 100 Hz in slices from naive mice. D, Summary of experiments showing the effect of OXT (0.1 μm) on evoked IPSCs in CA2 pyramidal neurons in slices from WT and Oxtr−/− mice. E, Summary of experiments showing two train of 1 s HFS at 100 Hz induced LTD of IPSCs in CA2 pyramidal neurons in slices from WT and Oxtr−/− mice. F, A representative image showing the distribution of PVN projecting fibers in the SLM of the CA2. Sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Inset, OXT neurons in the PVN were labeled with anti-OXT antibody (red) and infected with AAV-Ubi-GFP. Scale bars: 200 μm; inset, 100 μm. SP, Stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum; 3V, third ventricle. Representative traces of EPSPs, EPSCs, or IPSCs were taken at the time indicated by number. Dashed lines show level of baseline. The total number of animals examined is indicated by n in parenthesis. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
