Figure 4.
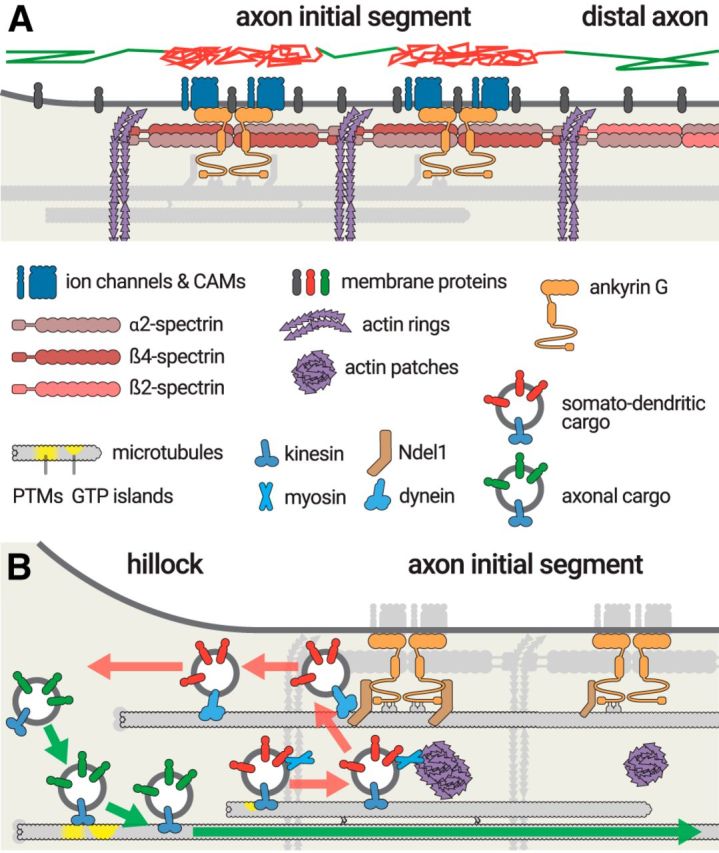
Protein trafficking at the AIS. A, The AIS forms a diffusion barrier for membrane proteins and lipids (gray). A virtual trajectory (top) shows unimpaired diffusion at the cell body and distal axon (green segments), whereas diffusion at the AIS is limited by the AIS scaffold (red segments). B, Sorting of transport vesicles at the AIS entrance. Vesicles containing axonal cargoes (green) have kinesin motors (blue) that recognize cues on microtubules entering the axon, either post-translational modifications or GTP islands (yellow), before being transported into the axon (green arrow). Somatodendritic cargoes that start progressing into the AIS (red) are stopped by myosin-mediated immobilization at actin patches, before being brought back to the cell body by Ndel1-dependendant dynein transport (red arrows).
