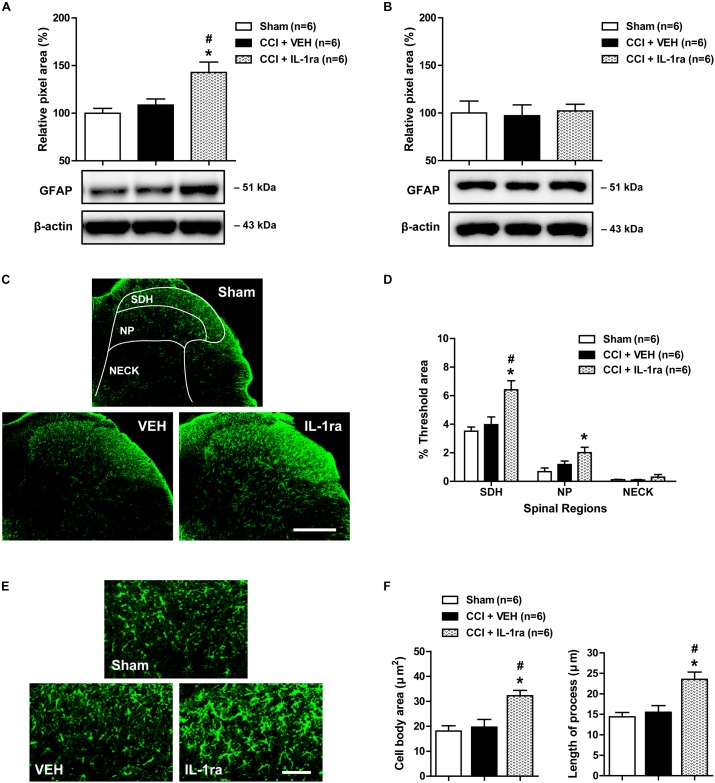
FIGURE 3.
Effects of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1ra, 20 ng) administration on the expression of GFAP in the lumbar spinal cord dorsal horn of CCI mice. (A) Results of Western blot analysis showing that the protein expression of GFAP did not change following CCI at day 1 post-CCI surgery, while administration of IL-1ra increased the expression of GFAP in the ipsilateral lumbar spinal cord dorsal horn. (B) The expression of GFAP in the contralateral dorsal horn did not show any change after CCI and IL-1ra administration. n = 6 mice/group. (C) Representative images showing the changes in GFAP expression at day 1 post-surgery in the ipsilateral lumbar spinal cord dorsal horn of CCI mice using immunohistochemistry. Scale bar = 200 μm. (D) The immunofluorescence of GFAP in the superficial dorsal horn (SDH, lamina I-II), nucleus proprius (NP, lamina III-IV) and neck region (NECK, lamina V-VI) of mice was quantitated using an image analysis system. GFAP-immunoreactivity did not change following CCI at day 1 post-CCI surgery, while the administration of IL-1ra increased the expression of GFAP in the ipsilateral lumbar spinal cord dorsal horn. (E) Higher magnification images are shown in panel (E). Scale bar = 40 μm. (F) The cell body area (μm2) and the length of processes (μm) radiating from the soma of astrocytes did not change following CCI at day 1 post-surgery, while administration of IL-1ra increased the cell body area (μm2) and the length of processes (μm). The spinal cord dorsal horn was sampled at day 1 post-surgery. n = 6 mice/group. ∗P < 0.05 vs. Sham; #P < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated group.