Figure 2.
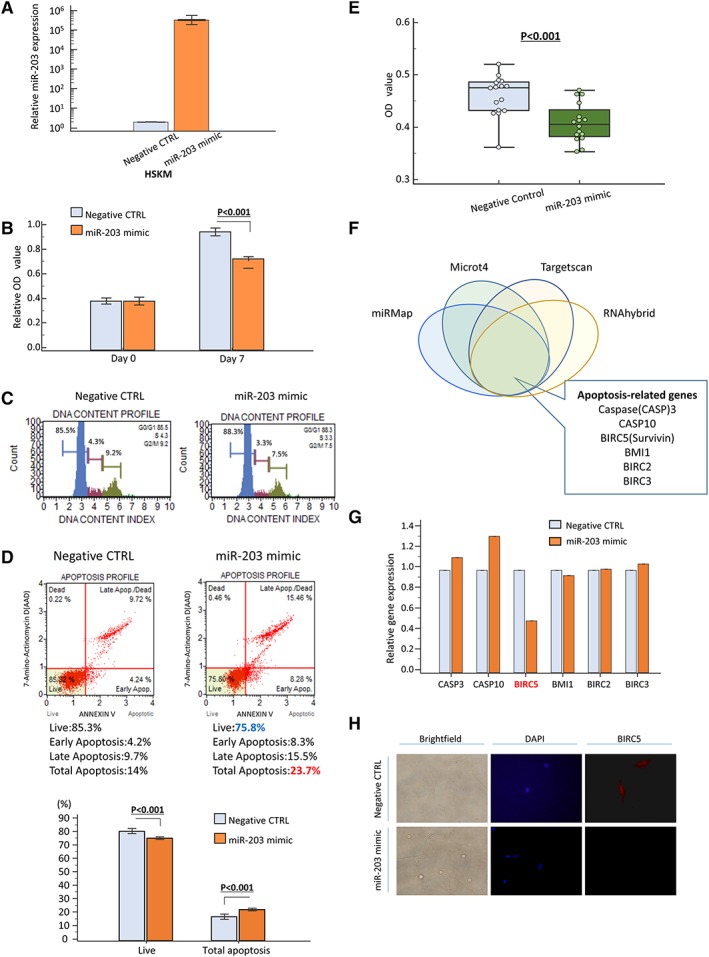
Series of in vitro analysis using human skeletal muscle cells (SkMCs). (A) Overexpression of miR‐203 expression 48 h after transfection in SkMC line. (B) Effect of miR‐203 overexpression on SkMC proliferation as assessed by MTT assay. (C) Cell cycle analysis demonstrated that G0/G1 fraction was increased after miR‐203 overexpression. (D, E) Apoptosis assay to investigate the population of apoptotic cells and viable cells of SkMCs after miR‐203 overexpression. Apoptosis rates were measured by annexin V and 7‐amino‐actinomycin D (7‐AAD) staining, and apoptotic cells were calculated as upper right and lower right (D): negative control (CTRL): right panel; miR‐203 mimic: left panel. Rate of apoptotic cells was significantly increased after miR‐203 overexpression (P < 0.05, lower panel). The number of viable cancer cells was also calculated by MTT assay and showed that miR‐203 up‐regulation decreased the number of viable SkMCs (E). (F) Prediction of miR‐203 target gene via four different miRNA target prediction tools (miRMap, Microt4, Targetscan, and RNAhybrid). (G) Expression profile of apoptosis‐related genes about putative targets of miR‐203 showed that overexpression of miR‐203 suppressed BIRC5 expression in SkMCs. Expression profile of apoptosis‐related genes about putative targets of miR‐203 showed that overexpression of miR‐203 suppressed BIRC5 expression in SkMCs. (H) BIRC5 protein was expressed in both nucleus and cytoplasm in SkMCs and was down‐regulated in miR‐203 mimic‐transfected cells compared with negative CTRL cells. Each value represents the mean ± standard error. OD, optical density.
