Figure 1.
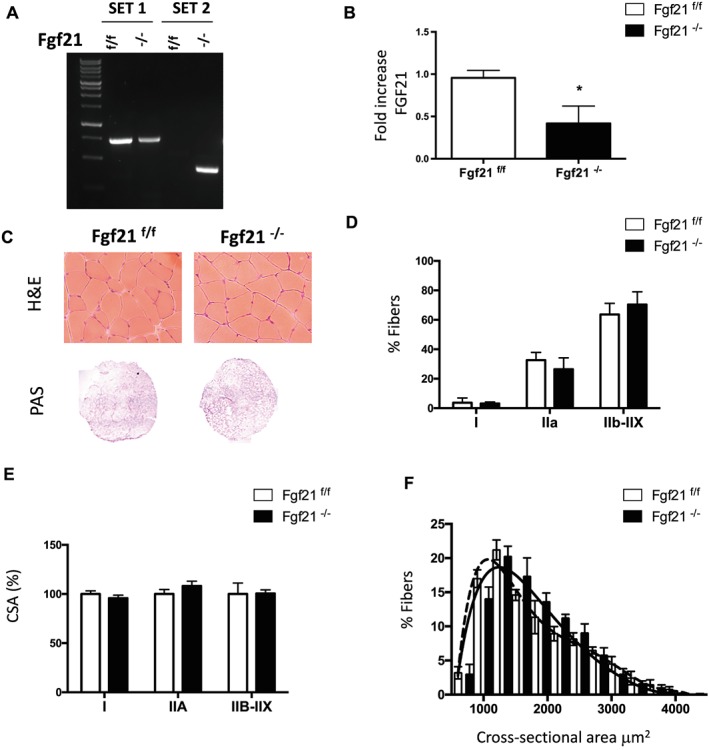
Muscle‐specific FGF21 deletion does not affect muscle size or histology. (A) Genotyping of FGF21 control and knockout mice. PCR analysis with genomic DNA from gastrocnemius muscles. Two sets of primers were used. Set 1 consists of one primer upstream of the 5′ loxP site and the other primer inside FGF21 sequence, amplifying a 675 bp sequence corresponding to not deleted DNA; set 2 consists of a couple of primers upstream 5′ loxP and downstream 3′ loxP sites that detects the deleted sequence. (B) FGF21 mRNA expression was quantified by q‐PCR in tibialis anterior muscle of FGF21−/− and control mice. (C) Representative H&E and PAS staining showing normal morphology, and glycogen content of FGF21−/− gastrocnemius muscle. (D) Percentage of fibres expressing myosin heavy chain types I, IIA, IIB, and IIX proteins in gastrocnemius muscles revealed by immunohistochemistry analysis. (E) Quantification of CSA of myofibers indicates no significant differences in FGF21‐ablated muscles. (F) Frequency histograms showing the distribution of cross‐sectional areas (μm2) in GNM of FGF21f/f (black dashed line) and FGF21−/− (black line) fibres. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. * P < 0.05. CSA, cross‐sectional area; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; H&E, haematoxylin and eosin; PAS, periodic acid–Schiff.
