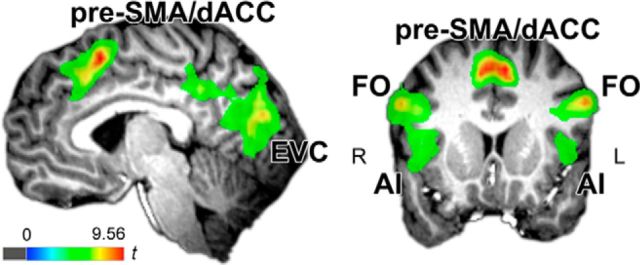
Figure 3.
Results from atypical versus typical contrast from whole-brain typicality × task group-level mixed effects repeated-measures ANOVA. Results indicate regions where responses were greater to atypical versus typical category targets on average across tasks (there were no interactions with task across the brain). Interestingly, we found that the cingulo-opercular network, the pre-SMA/dACC and FO/IA, responded more strongly to atypical than typical category members, suggesting potential involvement of conflict-monitoring processes in response to increased category coactivation and competition during atypical target perception. The pre-SMA/dACC cluster was used to construct an ROI for trial-by-trial analyses.