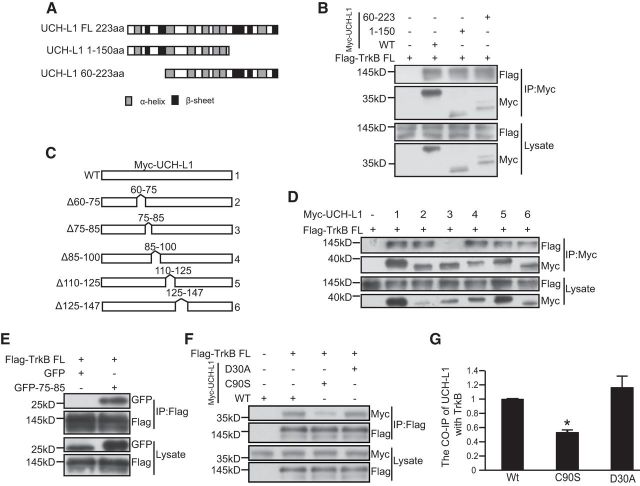
Figure 4.
The 75–85 aa region of UCH-L1 is necessary and sufficient for the interaction between UCH-L1 and TrkB. A, Schematic presentation of UCH-L1-FL, UCH-L1 1–150, and UCH-L1 60–223 used in this study. B, Co-IP was performed in HEK293 cell lysates expressing Myc UCH-L1 or UCH-L1 1–150 or UCH-L1 60–223 and Flag-TrkB FL. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-Myc antibodies and analyzed by immunoblotting with Flag antibodies. C, Schematic presentation of UCH-L1-FL and its deletion mutats. D, Co-IP was performed in HEK293 cell lysates expressing Myc UCH-L1 or its deletion mutants and Flag-TrkB. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) using anti-Myc antibodies and analyzed by immunoblotting with Flag antibodies. E, Co-IP was performed in HEK293 cell lysates expressing pEGFPC2 (GFP) or pEGFPC2-UCH-L175–85 (GFP-75–85) and Flag-TrkB FL. Cell lysates were IP using an anti-Flag antibodies and analyzed by immunoblotting with GFP antibodies. F, Co-IP was performed in HEK293 cell lysates expressing Myc UCH-L1 or its mutants and Flag-TrkB. Cell lysates were IP using an anti-Flag antibodies and analyzed by immunoblotting with Myc antibodies. G, Quantification of the affinity between TrkB FL and UCH-L1 or mutants of UCH-L1. *p < 0.05 versus WT UCH-L1, one-way ANOVA.