Figure 3.
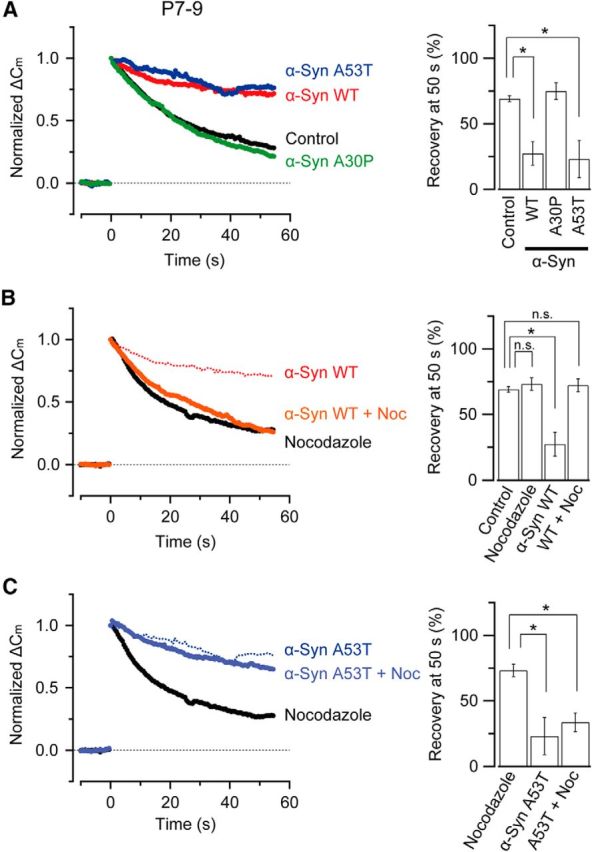
α-Synuclein A53T mutant inhibits vesicle endocytosis at calyces of Held in prehearing rats in a MT-independent manner. A, In rat calyces of Held from prehearing rats (P7–P9), both WT α-synuclein (His tag, 3.6 μm, n = 5, red) and A53T (3.6 μm, n = 5, blue) inhibited endocytic capacitance change elicited by a 20 ms depolarizing pulse (p < 0.05), whereas the A30P mutant (3.6 μm, n = 5, green) had no effect (p = 0.42). Bar graphs indicate mean endocytic recovery (%) from exocytic ΔCm 50 s after stimulation. B, Endocytic inhibition by WT α-synuclein (His tag) rescued by nocodazole (10 μm, n = 4–5, no significant difference between nocodazole alone and WT α-synuclein + nocodazole, p = 0.89). C, Endocytic inhibition by the A53T mutant could not be rescued by nocodazole (10 μm, n = 4–5, significant difference between nocodazole alone and A53T + nocodazole, p < 0.05). Asterisks indicate a significant difference (*p < 0.05).
