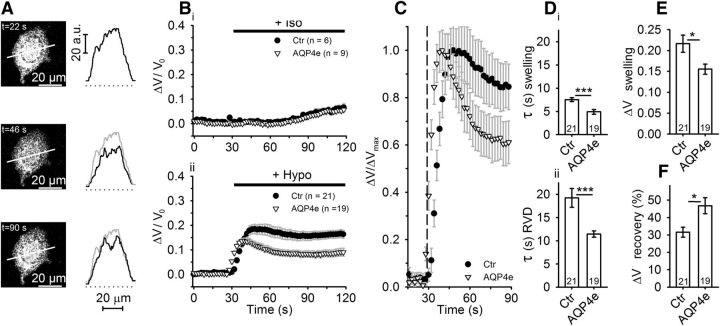
Figure 4.
Astrocytes overexpressing AQP4e exhibit a faster but smaller increase in cell volume in hypoosmotic conditions. A, An astrocyte labeled by SR101, before (t = 22 s) and after stimulation with hypotonic milieu (at t = 46 s and t = 90 s, respectively). Graphs adjacent to the micrographs represent fluorescence intensity profiles obtained along the line denoted in respective micrographs. Gray line represents fluorescence intensity profile at t = 22 s. B, The relative volume changes, obtained by measuring the average fluorescence intensity of SR101 of the whole cell, in control untransfected (Ctr) and in AQP4e-overexpressing (AQP4e) astrocytes in isoosmotic (Iso; Bi) and Hypo conditions (Bii). C, Normalized time-dependent changes in the volume shown in Bii. Bii, C, Note the smaller peak of the response (i.e., swelling; Bii) and the better recovery (of the cell volume in RVD) in cells overexpressing AQP4e compared with untransfected controls (C). The kinetics of the volume change was faster in cells overexpressing AQP4e. The dashed line represents the application of hypotonic solution. D, Time constants (in seconds) of the swelling phase (Di) were on average significantly smaller in cells overexpressing AQP4e (4.9 ± 0.5) than in control untransfected cells (7.5 ± 0.4). The RVD phase (Dii) occurred faster in transfected cells (11.4 ± 0.7) than in control untransfected cells (19.2 ± 2.0). E, Maximal amplitude of the volume increase (ΔV swelling) was smaller in cells overexpressing AQP4e (0.16 ± 0.01 A.U.) than in controls (0.22 ± 0.02 A.U.; p = 0.02). F, Recovery of the cell volume in the RVD phase was higher in cells overexpressing AQP4e (Ctr, 31.6 ± 2.8%; AQP4e, 46.8 ± 4.6%; p = 0.02). Numbers in the bars or brackets represent the number of cells analyzed. Student's t test was used for statistical comparison: *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001.