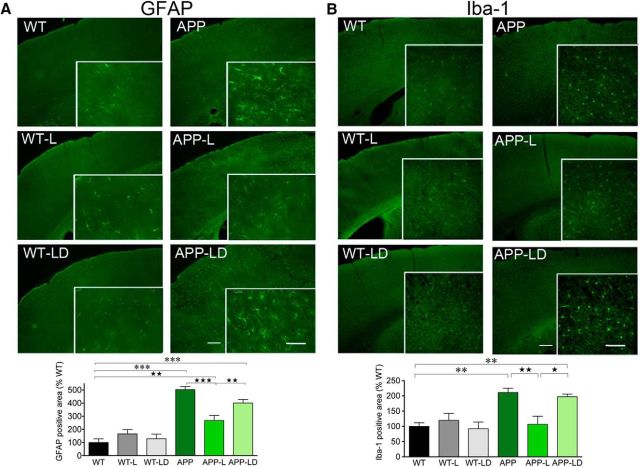
Figure 4.
Divalinal reduced losartan's benefits on astrogliosis and microgliosis in APP mice. The surface area occupied by GFAP-immunostained astrocytes was significantly increased in the cortex of APP mice relative to WT (A). Losartan (L) significantly reduced this inflammatory response, a benefit partly but significantly reversed by combined losartan + divalinal (LD) treatment (A). Similarly, Iba-1-immunopositive microglial cells were elevated in APP mice compared with WT and reduced after L treatment (B), a response almost abolished by D (B). Results were analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by Newman–Keuls post hoc test. Comparisons with WT are indicated by **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 and with APP L-treated mice by ★p < 0.05, ★★p < 0.01, and ★★★p < 0.001. n = 4–5 mice/group. Error bars indicate SEM. Scale bars, 0.5 and 500 μm.