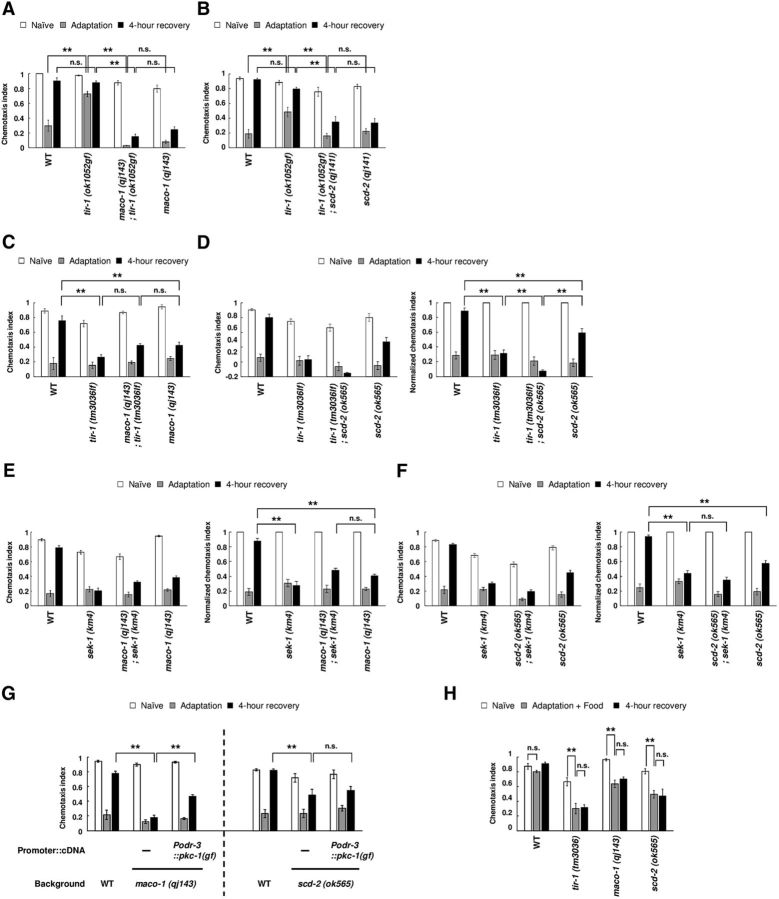
Figure 1.
MACO-1 and SCD-2 regulate forgetting of adaptation to diacetyl downstream of TIR-1. A, Genetic interaction between tir-1 (ok1052gf) and maco-1 (qj143). Chemotaxis of naive, adapted, and 4-h-recovered animals were used (n = 8, 2-way ANOVA, Fstrain(3,84) = 149.8, p < 0.001). B, Genetic interaction between tir-1 (ok1052gf) and scd-2 (qj141; n = 8, 2-way ANOVA, Fstrain(3,84) = 31.4, p < 0.001). C, Genetic interaction between tir-1 (tm3036lf) and maco-1 (qj143; n ≥ 16, 2-way ANOVA, Fstrain(3,276) = 25.9, p < 0.001). D, Genetic interaction between tir-1 (tm3036lf) and scd-2 (ok565). Chemotaxis and normalized chemotaxis were used (n ≥ 18, 2-way ANOVA, Fstrain(3,312) = 28.1, p < 0.001). E, Genetic interaction between sek-1 (km4) and maco-1 (qj143). Chemotaxis and normalized chemotaxis were used (n = 16, 2-way ANOVA, Fstrain(3,180) = 10.7, p < 0.001). F, Genetic interaction between sek-1 (km4) and scd-2 (ok565). Chemotaxis and normalized chemotaxis were used (n = 22, 2-way ANOVA, Fstrain(3,252) = 16.1, p < 0.001). G, Effect of PKC-1 (gf) expression, which activates neural secretion. PKC-1 (gf) was expressed in AWC sensory neurons of maco-1 (qj143) and scd-2 (ok565) mutant animals [n ≥ 6, maco-1 (qj143): 2-way ANOVA, Fstrain(2,63) = 48.4, p < 0.001; scd-2 (ok565): Fstrain(2,45) = 6, p = 0.0049]. H, Adaptation to diacetyl and its retention after conditioning with food in wild-type animals, and in tir-1 (tm3036lf), maco-1 (qj143), and scd-2 (ok565) mutant animals (n = 6, two-way ANOVA, Ftreatment(2,45) = 30.2, p < 0.001). **p < 0.01; post hoc t test with Bonferroni's correction. Error bars represent SEM.