Figure 3.
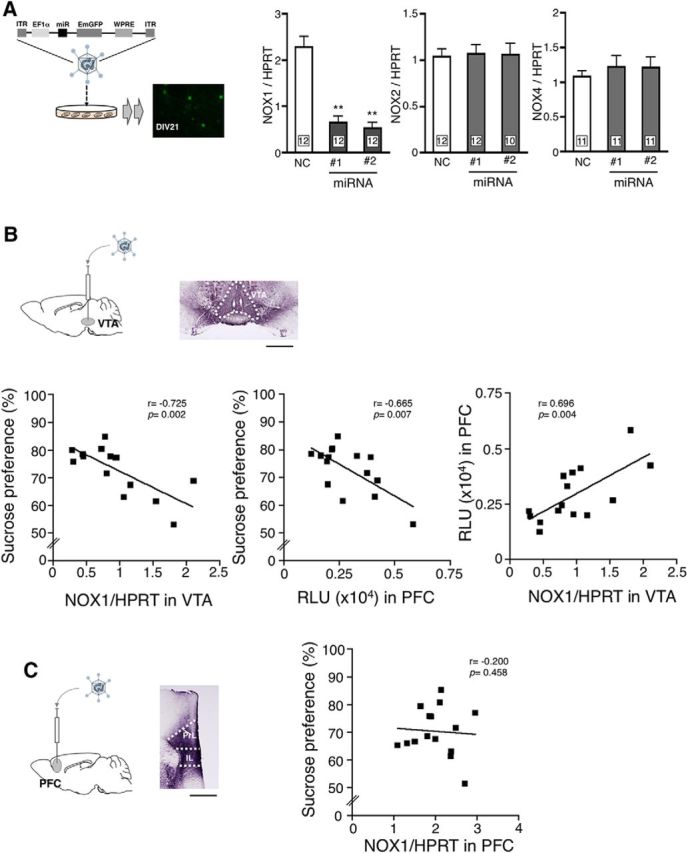
Increased NOX1 expression in VTA correlates with depressive-like behavior. A, Schematic diagram of gene silencing of NOX1 in primary cortical neurons using AAV2/rh10 coding miRNA against NOX1. The top demonstrates the structure of AAV-expressing cassettes harboring the artificial miRNA sequence and EmGFP. To verify the effects of miRNA on NOX1 expression, cultured embryonic neurons were infected with AAV2/rh10 expressing miRNA against NOX1 at DIV2. The total RNA in cultures was isolated at DIV21 when the fluorescence of GFP could be detected. Right panels indicate levels of NOX1, NOX2, and NOX4 mRNAs in cultured neurons transduced with AAV2/rh10 expressing the negative control (NC) or miRNAs against NOX1 (NOX1: F(2,33) = 37.66, p < 0.01, Bonferroni's post hoc test following one-way ANOVA; **p < 0.01 compared with NC; NOX2: F(2,31) = 0.02, p = 0.978; NOX4: F(2,30) = 0.31, p = 0.736). B, Correlations between sucrose preference and the level of NOX1 mRNA in VTA (left) or superoxide production in PFC (middle) of mice transduced on injection of AAV2/rh10 into VTA. Schematic diagram and a representative photomicrograph of GFPs expressed in VTA are shown. The right panel represents the correlation between superoxide production in PFC and the level of NOX1 mRNA in VTA. Mice were administered CORT for 21 d starting 3 weeks after viral injection. Values were obtained from 15 animals. Immunohistochemistry was performed at 6 weeks after virus injection. Scale bar, 500 μm. C, No correlation between sucrose preference and the level of NOX1 mRNA in PFC of mice transduced with AAV2/rh10 into PFC. Values were obtained from 16 animals. Scale bar, 500 μm. PrL, Prelimbic; IL, infralimbic.
