Figure 5.
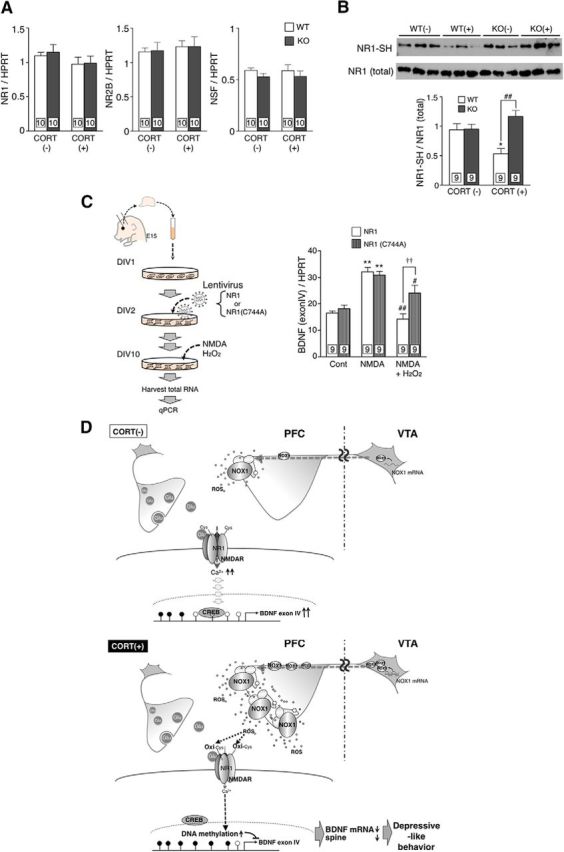
NR1 was a target molecule of NOX1-derived ROS in PFC. A, Levels of NR1, NR2B, and NSF mRNAs in PFC of mice treated with CORT. B, Assessment of the redox state of NR1 by the biotin pull-down assay. Top, NR1 bound to maleimide-(PEG)2-biotin, which corresponds to the protein containing reduced cysteine residues. Bottom, Total NR1 in the lysate. The graph demonstrates the ratio of NR1 containing reduced cysteine residues to total NR1 following quantitative densitometric analyses. *p < 0.05 compared with WT/CORT(−) and ##p < 0.01. C, Levels of exon IV-containing BDNF transcript in cortical neurons infected with lentivirus encoding NR1 or mutant NR1. **p < 0.01 compared with control and ##p < 0.01, #p < 0.05 compared with NMDA alone. ††p < 0.01. D, A hypothetical model of NOX1-mediated depressive-like behaviors. CORT-induced upregulation of NOX1 mRNA in VTA elicits increased ROS generation in PFC. Oxidation of cysteine residues of NR1 attenuates NMDA receptor activity, leading to increased DNA methylation in the promoter region of the bdnf gene, downregulation of BDNF, and the subsequent development of depressive-like behaviors.
