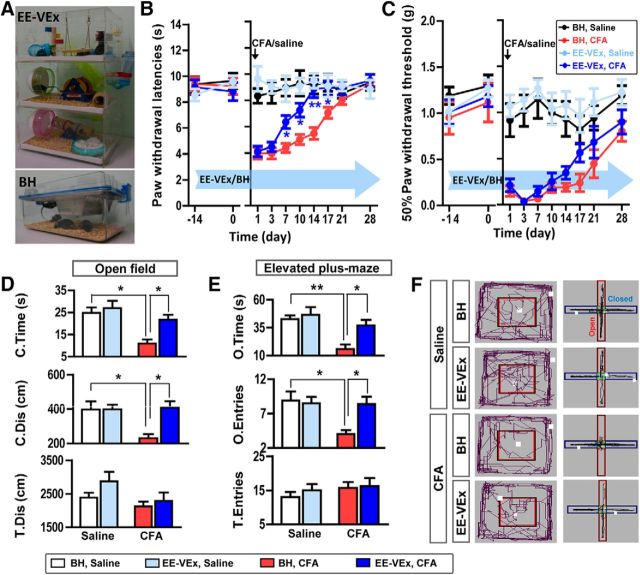
Figure 1.
EE-VEx attenuated thermal hyperalgesia, mechanical allodynia, and anxiety-like behaviors in chronic inflammatory pain. A, Representative photographs of EE-VEx (top) and BH (bottom) conditions. B, C, EE-VEx attenuated thermal hyperalgesia (B) and mechanical allodynia (C) in CFA-induced chronic inflammatory pain, without affecting baseline pain thresholds. n = 8 in each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, EE-VEx plus CFA vs BH plus CFA, ANOVA with repeated measures and Bonferroni's post hoc test. D, EE-VEx attenuated pain-induced anxiety-like behaviors in the open-field test. Persistent pain (14 d after CFA injection) decreased the time spent (top) and distance traveled (middle) in the central area of the open field, which were reversed by EE-VEx. Total distance traveled (bottom) in the field remained statistically similar across groups. n = 8 in each group. *p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test. E, EE-VEx attenuated pain-induced anxiety-like behaviors in the elevated plus-maze test. Chronic pain decreased the time spent (top) and entries (middle) into the open arms, which were reversed by EE-VEx. Total arm entries (bottom) were not affected. n = 8 in each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test. F, Representative exploratory tracks (black polylines) in the open field (left) and the elevated plus-maze (right).