Figure 3.
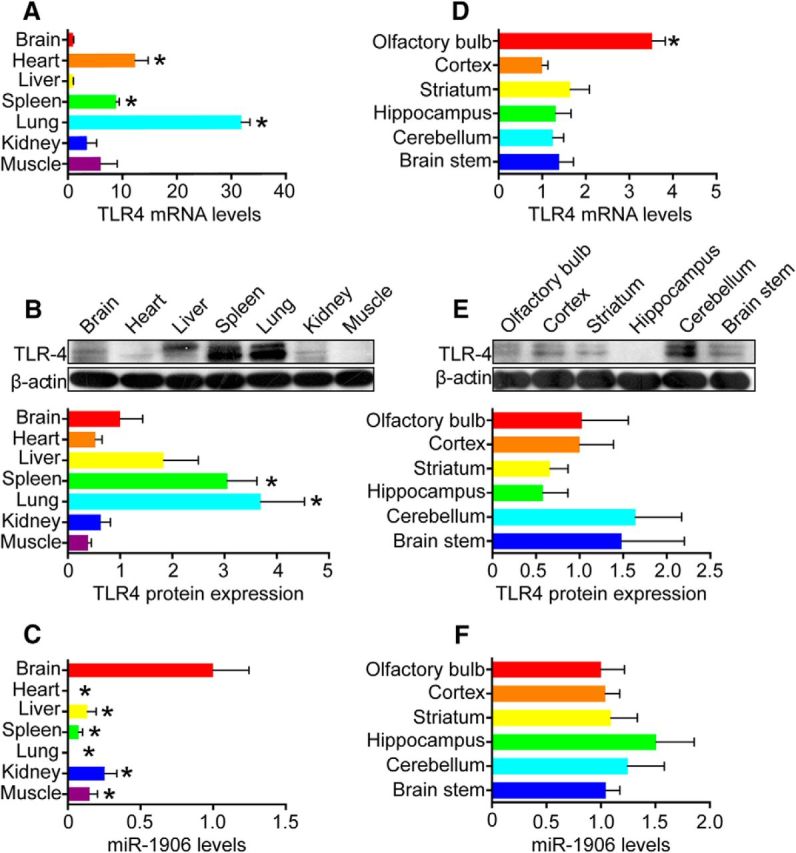
TLR4 and miR-1906 expression in major organs and the brain. A, B, TLR4 mRNA and protein levels in major organs relative to those in the brain as verified by PCR and WB. The TLR4 mRNA levels were higher in heart (p = 0.0003), spleen (p < 0.0001), and lung (p < 0.0001) tissue. The TLR4 protein levels in spleen (p = 0.0280) and lung (p = 0.0291) tisuse were higher than those in the brain (Student's t test, n = 6 for PCR, n = 4 for WB). C, miR-1906 levels in major organs relative to those in the brain. Compared with heart (p = 0.0024), liver (p = 0.0067), spleen (p = 0.0039), lung (p = 0.0024), kidney (p = 0.0169), and muscle (p = 0.0072) tissue, the brain showed significant miR-1906 enrichment (Student's t test, n = 6). D, E, TLR4 mRNA and protein levels in different regions of the brain relative to the cortex. F, miR-1906 levels in different regions of the brain. The TLR4 mRNA levels were significantly higher in the olfactory bulb than in the cortex (p < 0.0001). No significant difference was detected between the cortex and other cerebral regions (Student's t test, n = 6). Expression of the TLR4 protein (Student's t test, n = 4) and miR-1906 (Student's t test, n = 6) was statistically equivalent in each cerebral region compared with those in the cortex. *p < 0.05 by Student's t test, n as indicated.
