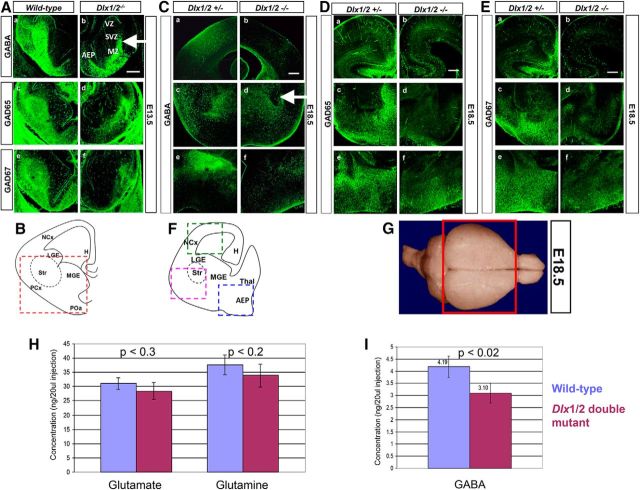
Figure 5.
A–F, GABA expression in the developing forebrain of Dlx1/2 wild-type compared with Dlx1/2 DKO mice. A, In the E13.5 wild-type, GABA (Aa), GAD65 (Ac), and GAD67 (Ae) expression is predominantly localized to the SVZ and MZ of the AEP and LGE compared with that in the absence of Dlx1 and Dlx2 function (Ab, Ad, Af). B, Schematic diagram of coronal section of the E13.5 forebrain, showing basal telencephalon in red dashed box. In the E18.5 wild-type, (C) GABA, (D) GAD65, (E) GAD67 expression is shown in neocortex (Ba), striatum (Bc), and AEP (Be) compared with the Dlx1/2 double mutant (Bb, Bd, Bf). F, Schematic diagram of coronal section of the E18.5 forebrain, showing neocortex (green dashed box), striatum (pink dshed box), and AEP (blue dashed box). Scale bars, 200 μm. H, Hippocampus; LGE, lateral ganglionic eminence; NCx, neocortex; PCx, paleocortex; POa, anterior preoptic area; Str, striatum. G–I, GABA levels are reduced in the Dlx1/2-null forebrains using HPLC. G, Forebrains of wild-type and Dlx1/2 double-mutant were dissected as depicted in the red box of the diagram. H, In the E18.5 forebrain, glutamate and glutamine (precursors of GABA) levels do not change when comparing wild-type and Dlx1/2 knock-out forebrain (excluding the olfactory bulbs). I, GABA neurotransmitter level decreases by ∼26% in the Dlx1/2 knock-out compared with wild-type forebrain. Homoserine was used as internal control. Sample concentrations were measured from standard curves and expressed as nanogram per 20 μl injection into the HPLC apparatus. Average ± SEM with associated p values.