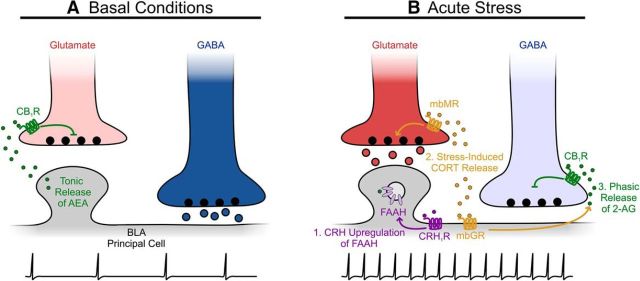
Figure 1.
Glucocorticoids interact with the endocannabinoid system following acute stress exposure to shift excitation/inhibition balance in the BLA. A, Under basal conditions, tonic release of AEA from BLA principal neurons dampens glutamate release by binding to presynaptic CB1Rs, while GABA release is unrestrained. Thus, inhibition dominates the network and presumably suppresses principal neuron firing. B, Following exposure to acute stress, (1) CRH released from cells in PVN activates its receptor (CRH1R) on BLA principal neurons, thus upregulating FAAH activity and halting the tonic release of AEA; (2) glucocorticoids (CORT) produced by the HPA axis bind presynaptic mbMRs to enhance glutamate release, and, simultaneously, CORT binds glucocorticoid receptors (mbGR) on principal cells (3) to trigger the retrograde release of 2-AG, which activates presynaptic CB1Rs to selectively suppress GABA release. Under these conditions, excitation dominates the network and presumably increases the principal neuron firing rate.