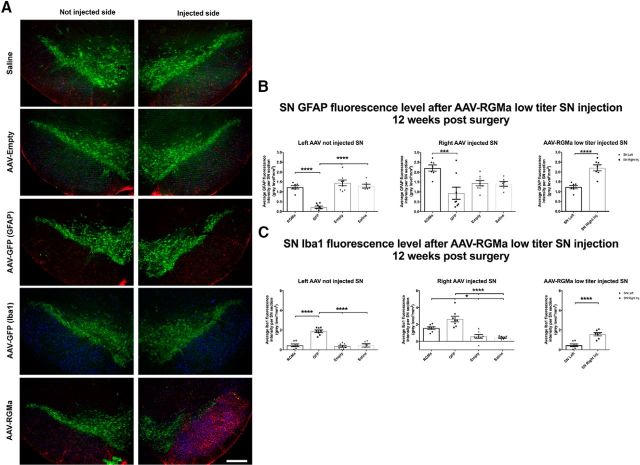
Figure 9.
Low-dose AAV-mediated overexpression of RGMa induced a gliotic response. A, Immunohistochemical staining for TH (green), GFAP (red), and Iba1 (blue) in mouse SN injected with saline, AAV-Empty, AAV-GFP, or AAV-RGMA. The two panels represent the injected and noninjected SN for each animal. Because of a limitation of the available number of fluorescence channels, two series of SN tissue were used for animals injected with AAV-GFP: one to stain for GFAP and one to stain for Iba1. B, Quantification of GFAP fluorescence signal in the SN 12 weeks after injection. Overexpression of RGMa in the SN is associated with an increase in GFAP fluorescence intensity in the injected SN compared with the AAV-GFP group (p = 0.0020, F(3,25) = 6.583) and to the noninjected SN in AAV-RGMa-treated animals (p < 0.0001). GFAP fluorescence is decreased in the noninjected SN of AAV-GFP-treated animals compared with the noninjected SN of the AAV-RGMa, AAV-Empty, and saline-treated groups (p < 0.0001, F(3,25) = 32.97). C, Quantification of Iba1 fluorescence signal in the SN 12 weeks after injection. Overexpression of RGMa in the SN is associated with an increase in Iba1 fluorescence intensity in the injected SN compared with the contralateral noninjected SN in RGMA-treated animals (p < 0.0001), as well as to the injected SN of the AAV-Empty and saline-treated animals (p < 0.0001, F(3,25) = 19.66). Iba1 fluorescence is significantly increased in both SN of animals injected with AAV-GFP compared with both SN of AAV-RGMa, AAV-Empty, and saline-treated animals (not injected SN, p < 0.0001, F(3,25) = 35.26; injected SN, p < 0.0001, F(3,25) = 19.66). AAV-RGMa treatment group consists of 7 animals, AAV-GFP and AAV-Empty consist of 8 animals per group, and the saline treatment group contains 6 animals. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc multiple testing correction and Student's t test: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. Scale bars, 0.25 mm. All data are expressed as mean with bars representing SEM.