Figure 4.
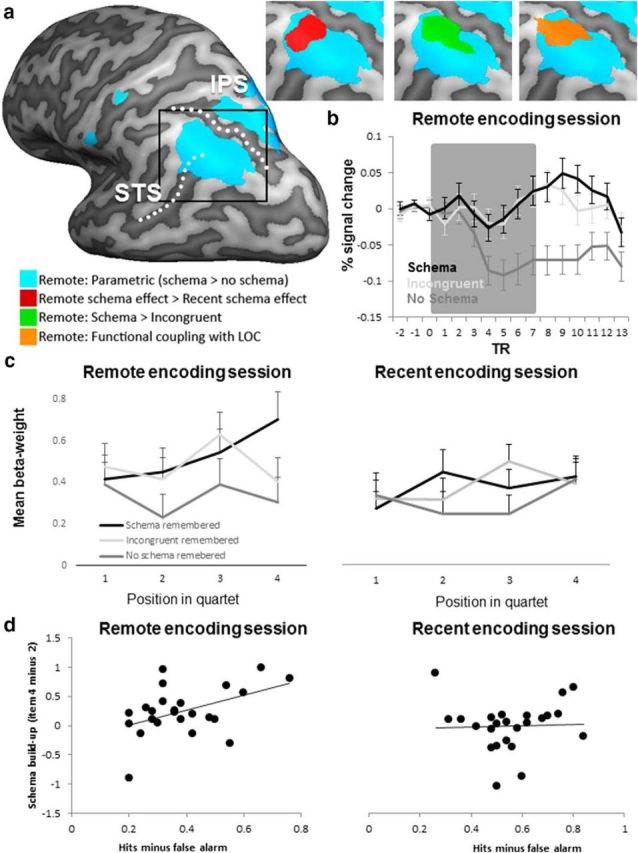
Schema effects in the AG during encoding. a, Inflated hemisphere (left hemisphere, dark gray areas are sulci) with overlays of four contrasts that all converge in the AG. In green are the areas that were more active in the remote encoding session to schema than to incongruent remembered final objects. In orange are areas that showed functional coupling with the LOC during encoding of subsequently remembered schema objects. In red are areas that showed a larger schema effect in the remote encoding session compared with the recent encoding session as follows: (remote schema remembered > remote no-schema remembered) > (recent schema remembered > no-schema remembered). In blue are areas that showed a parametric schema effect; that is, a buildup of activation with each object presentation (parametrically modulated activity during schema quartets > parametrically modulated activity during no-schema quartets). The dotted lines present the superior temporal sulcus (STS) and intraparietal sulcus (IPS) and are depicted for anatomical reference. All maps were corrected at a cluster level of p < 0.05 (voxel-level threshold was p < 0.001). b, Subject-averaged event-related time course from the AG region defined by the contrast: remote (schema > no-schema) > recent (schema > no-schema) and presented by the red area in a. We plotted the percentage signal change at each TR (2190 ms) for the three schema conditions (black: schema, light gray: incongruent, dark gray: no schema). The gray area indicates the time of the presentation of the quartet; the first object is presented at TR = 0 and the offset of the final object of the quartet is on average (with jittered intervals) at TR = 7. Error bars indicate SEM. c, For each encoding session, we plotted the subject-averaged β-weight for each of the four objects in the quartet from the same ROI as used in b. Schema quartets are in black, incongruent quartets are in light gray, and no-schema quartets are in dark gray. d, Correlation between the buildup of a schema (β-weight to object 4 minus β-weight to object 2) and the proportion of hits minus false alarms is plotted for both encoding sessions (from the same ROI used in b). The remote encoding session was the session 24 h before retrieval. The recent encoding session was the session immediately preceding retrieval.
